Artículos SCI
2022
2022
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Metal micromonoliths for the cleaning of H-2 by means of methanation reactions
Laguna, OH; Munoz-Murillo, A; Bobadilla, LF; Martinez, LM; Montes, M; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JACatalysis Today, 383 (2022) 216-225
Show abstract ▽
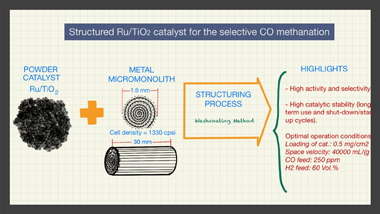
The present manuscript presents for the first time the structuring of a Ru/TiO2 catalyst that was achieved by means of the washcoating procedure using homemade metal micromonoliths (Fecralloy (R)) of 1330 cpsi. For this, an optimized formulation of the slurried catalyst as well as a reproducible protocol for the coating of the micromonoliths were successfully achieved. The obtained structured systems were tested in the selective CO methanation reaction and the effect of different variables over the catalytic performance were analyzed such as the amount of loaded catalyst in the micromonoliths, the temperature of reaction, the space velocity, and the amount of CO and H-2 within the feed-stream. The study of all of these parameters allowed to establish optimal conditions to maximize the performance of the structured Ru/TiO2 catalyst and subsequently, this was tested under those cited conditions in long-term tests (similar to 375 h), including shut-down/start-up cycles, aiming to evaluate its catalytic stability. The system presented a considerable stability along the different test without loss of catalytic activity, being specially remarkable its resistance to the inclusion of shut-down/start-up cycles. Therefore, this study lays the foundations for future development of more sophisticated structured systems for the selective CO methanation based on the structuring strategy proposed.
Enero, 2022 | DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2021.04.026
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
The Response of Tomato Fruit Cuticle Membranes Against Heat and Light
Benitez, JJ; Moreno, AG; Guzman-Puyol, S; Heredia-Guerrero, JA; Heredia, A; Dominguez, EFrontiers in Plant Science, 12 (2022) 807723
Show abstract ▽
Two important biophysical properties, the thermal and UV-Vis screening capacity, of isolated tomato fruit cuticle membranes (CM) have been studied by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and UV-Vis spectrometry, respectively. A first order melting, corresponding to waxes, and a second order glass transition (T-g) thermal events have been observed. The glass transition was less defined and displaced toward higher temperatures along the fruit ripening. In immature and mature green fruits, the CM was always in the viscous and more fluid state but, in ripe fruits, daily and seasonal temperature fluctuations may cause the transition between the glassy and viscous states altering the mass transfer between the epidermal plant cells and the environment. CM dewaxing reduced the T-g value, as derived from the role of waxes as fillers. T-g reduction was more intense after polysaccharide removal due to their highly interwoven distribution within the cutin matrix that restricts the chain mobility. Such effect was amplified by the presence of phenolic compounds in ripe cuticle membranes. The structural rigidity induced by phenolics in tomato CMs was directly reflected in their mechanical elastic modulus. The heat capacity (Cp-rev) of cuticle membranes was found to depend on the developmental stage of the fruits and was higher in immature and green stages. The average Cp-rev value was above the one of air, which confers heat regulation capacity to CM. Cuticle membranes screened the UV-B light by 99% irrespectively the developmental stage of the fruit. As intra and epicuticular waxes contributed very little to the UV screening, this protection capacity is attributed to the absorption by cinnamic acid derivatives. However, the blocking capacity toward UV-A is mainly due to the CM thickness increment during growth and to the absorption by flavone chalconaringenin accumulated during ripening. The build-up of phenolic compounds was found to be an efficient mechanism to regulate both the thermal and UV screening properties of cuticle membranes.
Enero, 2022 | DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2021.807723
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Au and Pt Remain Unoxidized on a CeO2-Based Catalyst during the Water-Gas Shift Reaction
Reina, TR; Gonzalez-Castano, M; Lopez-Flores, V; Martinez, LMT; Zitolo, A; Ivanova, S; Xu, WQ; Centeno, MA; Rodriguez, JA; Odriozola, JAJournal of the American Chemical Society, 144 (2022) 446-453
Show abstract ▽
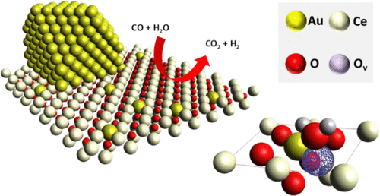
The active forms of Au and Pt in CeO2-based catalysts for the water-gas shift (WGS) reaction are an issue that remains unclear, although it has been widely studied. On one hand, ionic species might be responsible for weakening the Ce-O bonds, thus increasing the oxygen mobility and WGS activity. On the other hand, the close contact of Au or Pt atoms with CeO2 oxygen vacancies at the metal-CeO2 interface might provide the active sites for an efficient reaction. In this work, using in situ X-ray absorption spectroscopy, we demonstrate that both Au and Pt remain unoxidized during the reaction. Remarkable differences involving the dynamics established by both species under WGS atmospheres were recognized. For the prereduced Pt catalyst, the increase of the conversion coincided with a restructuration of the Pt atoms into cuboctahedrical metallic particles without significant variations on the overall particle size. Contrary to the relatively static behavior of Pt-0, Au-0 nanoparticles exhibited a sequence of particle splitting and agglomeration while maintaining a zero oxidation state despite not being located in a metallic environment during the process. High WGS activity was obtained when Au atoms were surrounded by oxygen. The fact that Au preserves its unoxidized state indicates that the chemical interaction between Au and oxygen must be necessarily electrostatic and that such an electrostatic interaction is fundamental for a top performance in the WGS process.
Enero, 2022 | DOI: 10.1021/jacs.1c10481
Materiales Avanzados
Study of a Waste Kaolin as Raw Material for Mullite Ceramics and Mullite Refractories by Reaction Sintering
Sanchez-Soto, PJ; Eliche-Quesada, D; Martinez-Martinez, S; Perez-Villarejo, L; Garzon, EMaterials, 15 (2022) 583
Show abstract ▽
A deposit of raw kaolin, located in West Andalusia (Spain), was studied in this work using a representative sample. The methods of characterization were X-ray diffraction (XRD), X-ray fluorescence (XRF), particle size analysis by sieving and sedimentation, and thermal analysis. The ceramic properties were determined. A sample of commercial kaolin from Burela (Lugo, Spain), with applications in the ceramic industry, was used in some determinations for comparison purposes. The kaolin deposit has been produced by alteration of feldspar-rich rocks. This raw kaolin was applied as an additive in local manufactures of ceramics and refractories. However, there is not previous studies concerning its characteristics and firing properties. Thus, the meaning of this investigation was to conduct a scientific study on this subject and to evaluate the possibilities of application. The raw kaolin was washed for the beneficiation of the rock using water to increase the kaolinite content of the resultant material. The results indicated that the kaolinite content of the raw material was 20 wt % as determined by XRD, showing ~23 wt % of particles lower than 63 mu m. The kaolinite content of the fraction lower than 63 mu m was 50 wt %. Thus, an improvement of the kaolinite content of this raw kaolin was produced by wet separation. However, the kaolin was considered as a waste kaolin, with microcline, muscovite and quartz identified by XRD. Thermal analyses by Thermo-Dilatometry (TD), Differential Thermal Analysis (DTA) and Thermo-Gravimetry (TG) allowed observe kaolinite thermal decomposition, quartz phase transition and sintering effects. Pressed samples of this raw kaolin, the fraction lower than 63 mu m obtained by water washing and the raw kaolin ground using a hammer mill were fired at several temperatures in the range 1000-1500 & DEG;C for 2 h. The ceramic properties of all these samples were determined and compared. The results showed the progressive linear firing shrinkage by sintering in these samples, with a maximum value of ~9% in the fraction lower than 63 mu m. In general, water absorption capacity of the fired samples showed a decrease from ~18-20% at 1050 & DEG;C up to almost zero after firing at 1300 & DEG;C, followed by an increase of the experimental values. The open porosity was almost zero after firing at 1350 & DEG;C for 2 h and the bulk density reached a maximum value of 2.40 g/cm(3) as observed in the ground raw kaolin sample. The XRD examination of fired samples indicated that they are composed by mullite, from kaolinite thermal decomposition, and quartz, present in the raw sample, as main crystalline phases besides a vitreous phase. Fully-densified or vitrified materials were obtained by firing at 1300-1350 & DEG;C for 2 h. In a second step of this research, it was examined the promising application of the previous study to increase the amount of mullite by incorporation of alumina (alpha-alumina) to this kaolin sample. Firing of mixtures, prepared using this kaolin and alpha-alumina under wet processing conditions, produced the increase of mullite in relative proportion by reaction sintering at temperatures higher than 1500 & DEG;C for 2 h. Consequently, a mullite refractory can be prepared using this kaolin. This processing of high-alumina refractories is favoured by a previous size separation, which increases the kaolinite content, or better a grinding treatment of the raw kaolin.
Enero, 2022 | DOI: 10.3390/ma15020583
2021
2021
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
In Situ DRIFTS-MS Methanol Adsorption Study onto Supported NiSn Nanoparticles: Mechanistic Implications in Methanol Steam Reforming
Bobadilla, LF; Azancot, L; Ivanova, S; Delgado, JJ; Romero-Sarria, F; Centeno, MA; Roger, ACNanomaterials, 11 (2021) 3234
Show abstract ▽
Methanol adsorption over both supported NiSn Nps and analogous NiSn catalyst prepared by impregnation was studied by in situ diffuse reflectance infrared Fourier transform spectroscopy (DRIFTS) to gain insights into the basis of hydrogen production from methanol steam reforming. Different intermediate species such as methoxides with different geometry (bridge and monodentate) and formate species were identified after methanol adsorption and thermal desorption. It is proposed that these species are the most involved in the methanol steam reforming reaction and the major presence of metal-support interface sites in supported NiSn Nps leads to higher production of hydrogen. On the basis of these results, a plausible reaction mechanism was elucidated through the correlation between the thermal stability of these species and the evolution of the effluent gas released. In addition, it was demonstrated that DME is a secondary product generated by condensation of methoxides over the acid sites of alumina support in an acid-catalyzed reaction.
Diciembre, 2021 | DOI: 10.3390/nano11123234
- ‹ anterior
- 61 of 410
- siguiente ›














