Artículos SCI
2019
2019
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Kinetic energy-induced growth regimes of nanocolumnar Ti thin films deposited by evaporation and magnetron sputtering
Alvarez, R.; Garcia-Valenzuela, A.; Rico, V; Garcia-Martin, J. M.; Cotrino, J.; Gonzalez-Elipe, A. R.; Palmero, A.Nanotechnology, 30 (2019) 475603
Show abstract ▽
We experimentally analyze different growth regimes of Ti thin films associated to the existence of kinetic energy-induced relaxation mechanisms in the material's network when operating at oblique geometries. For this purpose, we have deposited different films by evaporation and magnetron sputtering under similar geometrical arrangements and at low temperatures. With the help of a well-established growth model we have found three different growth regimes: (i) low energy deposition, exemplified by the evaporation technique, carried out by species with typical energies in the thermal range, where the morphology and density of the film can be explained by solely considering surface shadowing processes, (ii) magnetron sputtering under weak plasma conditions, where the film growth is mediated by surface shadowing mechanisms and kinetic-energy-induced relaxation processes, and (iii) magnetron sputtering under intense plasma conditions, where the film growth is highly influenced by the plasma, and whose morphology is defined by nanocolumns with similar tilt than evaporated films, but with much higher density. The existence of these three regimes explains the variety of morphologies of nanocolumnar Ti thin films grown at oblique angles under similar conditions in the literature.
Noviembre, 2019 | DOI: 10.1088/1361-6528/ab3cb2
Materiales Coloidales
Monodisperse Gold Cuboctahedral Nanocrystals Directly Synthesized in Reverse Micelles: Preparation, Colloidal Dispersion in Organic Solvents and Water, Reversible Self-Assembly and Plasmonic Properties
Luna, C; Castaneda-Rodriguez, D; Barriga-Castro, ED; Nunez, NO; Mendoza-Resendez, RLangmuir, 34 (2019) 14291-14299
Show abstract ▽
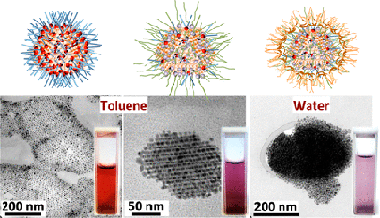
The synthesis of organic-solvent-dispersible gold nanoparticles in reverse micelles of didodecyldimethylammonium bromide (DDAB) is revisited in the present investigation. Some parameters of synthesis, specifically the reaction volume and the concentration of the reducing agent, were slightly modified obtaining directly monodisperse gold nanocrystals (AuNCs) without the need to use additional active surfactants or additional treatments such as digestive ripening. Interestingly, most of the obtained AuNCs display the same exposed crystalline faces composed of six bounding facets (four {111} faces and two {002} faces), corresponding to single-crystalline face-centered cubic nanoparticles with a cuboctahedron shape. When these AuNCs are subsequently functionalized with 1-decanethiol (C10H21SH) or 1-dodecanethiol (C12H25SH), they don’t experience significant changes in their size or crystalline texture, however, they self-aggregate directly in the suspension at room temperature into faceted supramolecular structures and exhibit collective plasmonic excitations. Such self-organization is reversible under heating treatments allowing the observation of the influence of the AuNCs aggregation state on their plasmonic properties. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy reveals that thiols only replace partially the DDAB molecules, and thus, DDAB molecules remain present in the thiol-capped AuNCs. To turn the thiol-capped nanocrystals into water-dispersible nanocrystals and extend their technological potential, they are stabilized with poloxamer 407 obtaining highly stable purple colloids in water.
Noviembre, 2019 | DOI: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.9b02374
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Morphological effects on the photocatalytic properties of SnO2 nanostructures
Kar, A; Olszowka, J; Sain, S; Sloman, SRI; Montes, O; Fernandez, A; Pradhan, SK; Wheatley, AEHJournal of Alloys and Compounds, 810 (2019) UNSP 151718
Show abstract ▽
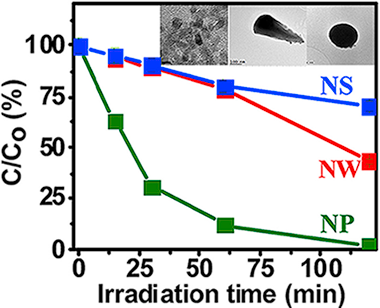
The photocatalytic properties of SnO2 nanocrystals are tuned by varying their morphology and microstructure. SnO2 nanoparticles and nanowedges have been synthesized using hydrothermal methods, while microwave irradiation techniques have given nanospheres. Detailed structural and chemical characterization of these different morphologies has been accomplished. The influence of SnO2 morphology on photocatalytic activity has been examined by monitoring the degradation of aqueous methylene blue dye. Results demonstrate that changing the morphology of the SnO2 modulates both surface area and levels of surface defects and that these alterations are reflected in the photocatalytic properties of the materials. The degradation of methylene blue dye (98%) in the presence of SnO2 nanoparticles under simulated solar irradiation is superior to previously reported photocatalyst performance and is comparable to that of standard TiO2 (Degussa P-25). The SnO2 nanoparticles perform better than both the nanowedges and nanospheres and this is attributed to the number of surface defects available to the high surface area material. They also reveal outstanding recyclability and stability.
Noviembre, 2019 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.151718
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Colombian metallurgical coke as catalysts support of the direct coal liquefaction
Rico, D; Agamez, Y; Romero, E; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JA; Diaz, JDFuel, 255 (2019) 115748
Show abstract ▽
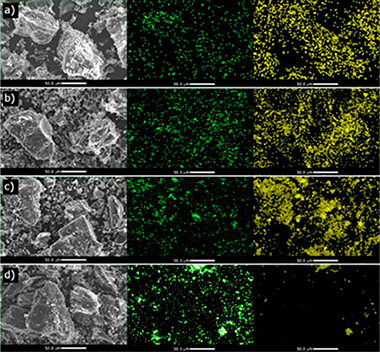
A Colombian metallurgical coke was modified in its surface chemistry and was used as support of iron sulfide catalysts for direct coal liquefaction. The modification was made by treatments with diluted oxygen and HNO3 at different conditions. Changes in surface chemistry were studied by determining the point of zero charge (PZC), the isoelectric point (IEP), thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), temperature programmed decomposition-mass spectrometry (TPD-MS), Diffuse-reflectance infrared Fourier transform spectroscopy (DRIFTS) and nitrogen adsorption at 77 K. The results show that the materials obtained have a wide range of functional groups incorporated in a different proportion and quantity. The textural parameters indicate that treatment with diluted oxygen increases the surface area and incorporates micropores while the samples treated with HNO3 maintain the textural properties of the original material. The catalysts were also characterized by Raman spectroscopy. It was found that impregnation with the iron sulfide precursor does not significantly affect the Raman characteristics of the support. Additionally, XRD analysis shows smaller pyrite crystallites in the coke enriched with oxygenated groups of phenol and lactone indicating better dispersion of the active phase. The amount of oxygen chemisorbed per gram of catalyst shows that both, oxygen and nitric acid treatments, improve the relative dispersion of the active phase. It was found that the presence of the catalysts increases the conversion and yields towards oils and gases with respect to those of the tests without catalysts. Cokes modified by dilute oxygen gaseous treatment contain surface phenol and lactone groups and present the highest yield to oils.
Noviembre, 2019 | DOI: 10.1016/j.fuel.2019.115748
Reactividad de Sólidos
The influence of mechanical activation process on the microstructure and mechanical properties of bulk Ti2AlN MAX phase obtained by reactive hot pressing
Salvo, C; Chicardi, E; Garcia-Garrido, C; Jimenez, JA; Aguilar, C; Usuba, J; Mangalaraja, RVCeramics International, 45 (2019) 17793-17799
Show abstract ▽
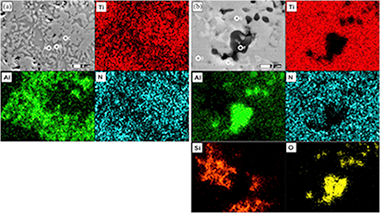
The effect of mechanical activation process on the microstructure and mechanical properties of bulk nanostructured Ti2AlN compound has been investigated in this work. The mixture of Ti and AlN powders was prepared in a 2:1 molar ratio, and a part of this powder was subjected to a high-energy milling process under argon atmosphere for 10 h using agate as grinding media. Finally, the densification and formation of the ternary Ti2AlN MAX phase through solid state reaction of both unmilled and milled powders were carried out by hot pressing under 15 or 30 MPa at 1200 degrees C for 2 h. The microstructure of precursor powder mixtures and the consolidated samples was characterized by using X-ray diffraction (XRD) and a scanning electron microscope equipped with an energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (SEM/EDS). The X-ray diffraction patterns were fitted using the Rietveld refinement for phase quantification and to determine their most important microstructural parameters. Microstructure and mechanical properties of the consolidated samples were correlated with the load used for the hot pressing process. The substantial increase of hardness, the higher densification and the lower grain sizes observed in the samples prepared from the activated powders were attributed to the formation of second phases like Ti5Si3 and Al2O3.
Octubre, 2019 | DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.05.350
- ‹ anterior
- 113 of 410
- siguiente ›














