Scientific Papers in SCI
2020
2020
Materiales Coloidales
Design of a nanoprobe for high field magnetic resonance imaging, dual energy X-ray computed tomography and luminescent imaging
Gonzalez-Mancebo, D; Becerro, AI; Corral, A; Garcia-Embid, S; Balcerzyk, M; Garcia-Martin, ML; de la Fuente, JM; Ocana, MJournal of Colloid and Interface Science, 573 (2020) 278-286
Show abstract ▽
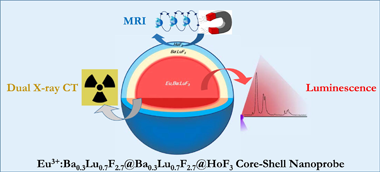
The combination of different bioimaging techniques, mainly in the field of oncology, allows circumventing the defects associated with the individual imaging modalities, thus providing a more reliable diagnosis. The development of multimodal endogenous probes that are simultaneously suitable for various imaging modalities, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), X-ray computed tomography (CT) and luminescent imaging (LI) is, therefore, highly recommended. Such probes should operate in the conditions imposed by the newest imaging equipment, such as MRI operating at high magnetic fields and dual-energy CT. They should show, as well, high photoluminescence emission intensity for their use in optical imaging and present good biocompatibility. In this context, we have designed a single nanoprobe, based on a core-shell architecture, composed of a luminescent Eu3+:Ba0.3Lu0.7F2.7 core surrounded by an external HoF3 shell that confers the probe with very high magnetic transverse relaxivity at high field. An intermediate, optically inert Ba0.3Lu0.7F2.7 layer was interposed between the core and the shell to hinder Eu3+-Ho3+ cross-relaxation and avoid luminescence quenching. The presence of Ba and Lu, with different K-edges, allows for good X-ray attenuation at high and low voltages. The core-shell nanoparticles synthesized are good potential candidates as trimodal bioprobes for MRI at high field, dual-energy CT and luminescent imaging.
August, 2020 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jcis.2020.03.101
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Hydrodeoxygenation of vanillin over noble metal catalyst supported on biochars: Part II: Catalytic behaviour
Santos, JL; Maki-Arvela, P; Warna, J; Monzon, A; Centeno, MA; Murzin, DYApplied Catalysis B-Environmental, 268 (2020) 118425
Show abstract ▽
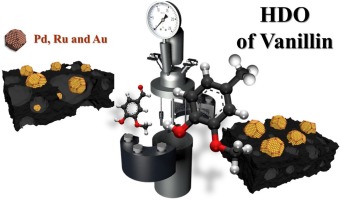
Vanillin hydrodeoxygenation was investigated using noble metal (Pd, Au, Ru) supported on active carbon prepared from waste derived biochars, which were produced via pyrolysis in CO2 atmosphere. Chemical activation with ZnCl2 and HNO3 was also used in the preparation of active carbon to enhance the specific surface area and demineralize material, respectively. Both fresh and spent catalysts were characterized with X-ray diffraction, DRIFTS, zeta potential measurement and HR-TEM. The highest selectivity to p-creosol, 92 % selectivity at complete vanillin conversion after 3 h was obtained in vanillin hydrodeoxygenation at 100 degrees C under 30 bar in hydrogen in water with Pd/C catalyst prepared via pyrolysis under CO2 from wine waste and using ZnCl2 as a chemical activation agent. Hydrodeoxygenation activity increased with increasing metal dispersion. A kinetic model including adsorption of vanillin described well the experimental data.
July, 2020 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.118425
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Performance trends in wall-flow diesel particulate filters: Comparative analysis of their filtration efficiency and pressure drop
Orihuela, MP; Chacartegui, R; Gomez-Martin, A; Ramirez-Rico, J; Villanueva, JABJournal of Cleaner Production, 60 (2020) 12063
Show abstract ▽
Soot and particulate emissions from the transport sector are a major concern worldwide, given their harmful effects on public health and the environment. On-road vehicles are the main contributing source to this kind of pollution. They are strictly regulated in many countries, with limitations on the number and concentration of released particles, and they must be equipped with particle abatement systems. Wall-flow particulate filters are the most popular and effective devices to reduce particulate emissions from diesel and gasoline vehicles. Diesel Particulate Filters (DPFs) have been a recurrent research topic since the last century. There are different research studies analysing different aspects of these systems, at different levels, using different methodologies and different approaches. Their results are not always comparable. This work analyses the latest advances and trends in this technology by comparing two relevant performance parameters: their filtration efficiency and pressure drop. The findings of this study suggest that, in order to be competitive, upcoming DPFs should have filtration efficiencies above 80%, and pressure drops below 10 kPa, for space velocities of 1.5.10(5) h(-1) or more at the clean state. They should reach similar to 100% efficiency after a short operation period, before the soot load reaches 0.2 g/L. Later, they should keep a low pressure drop for a longer time, with a reference of no more than 13 kPa for 6 g/L of soot load. Based on this analysis, this work proposes some test criteria and suggestions for the main parameters.
July, 2020 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.120863
Reactividad de Sólidos
Calcium-Looping Performance of Biomineralized CaCO3 for CO2 Capture and Thermochemical Energy Storage
Arcenegui-Troya, J; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Perejon, A; Valverde, JM; Chacartegui, R; Perez-Maqueda, LAIndustrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 59 (2020) 12924-12933
Show abstract ▽
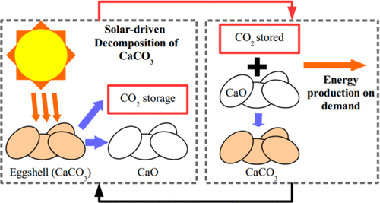
The commercial deployment of calcium-looping (CaL)-based technologies relies on the availability of nontoxic, widely available and cheap CaCO3 rich materials. Biomineralized CaCO3 from waste amply fulfills the aforementioned requirements. In the present work, we study the performance of eggshell and snail shell from food waste as CaO precursors for CaL applications. The results obtained suggest the feasible use of these waste materials. The multicyclic conversion exhibited by biomineralized CaCO3 was comparable to that demonstrated by limestone, which is a commonly proposed material for CaL applications. In addition, the temperature needed to completely calcine biomineralized CaCO3 in short residence times is lower than that required to fully calcine limestone. This would mitigate the energy cost of the technology.
July, 2020 | DOI: 10.1021/acs.iecr.9b05997
Reactividad de Sólidos
ICTAC Kinetics Committee recommendations for analysis of multi-step kinetics
Vyazovkin, S; Burnham, AK; Favergeon, L; Koga, N; Moukhina, E; Perez-Maqueda, LA; Sbirrazzuoli, NThermochimica Acta, 689 (2020) 178597
Show abstract ▽
The present recommendations have been developed by the Kinetics Committee of the International Confederation for Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry (ICTAC). The recommendations provide guidance on kinetic analysis of multi-step processes as measured by thermal analysis methods such as thermogravimetry (TGA) and differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). Ways of detecting the multi-step kinetics are discussed first. Then, four different approaches to evaluation of kinetic parameters (the activation energy, the pre-exponential factor, and the reaction model) for individual steps are considered. The approaches considered include multi-step model-fitting as well as distributed reactivity, isoconversional, and deconvolution analyses. For each approach practical advice is offered on its effective usage. Due attention is also paid to the typical problems encountered and to the ways of resolving them. The objective of these recommendations is to help a non-expert with efficiently performing multi-step kinetic analysis and interpreting its results.
July, 2020 | DOI: 10.1016/j.tca.2020.178597
- ‹ previous
- 96 of 410
- next ›














