Scientific Papers in SCI
2020
2020
Tribología y Protección de Superficies
Tribological performance of Nb-C thin films prepared by DC and HiPIMS
Sala, N; Abad, MD; Sanchez-Lopez, JC; Cruz, M; Caro, J; Colominas, CMaterials Letters, 277 (2020) 12834
Show abstract ▽
Nanostructured NbC thin films with variable contents of Nb and C were prepared by direct current (DC) magnetron sputtering, and for the first time, via high power impulse magnetron sputtering (HiPIMS) searching for an improvement in the tribological properties. X-ray diffraction shows that increasing the carbon incorporation, the crystalline composition evolves from Nb2C to NbC phase. Further carbon enrichment leads to a nanocomposite structure formed by small NbC crystals (8-14 nm) dispersed in a-C matrix. The friction coefficient varied from high friction (0.8) to low friction (0.25) and the hardness values between 20 and 11 GPa depending on the film composition. A densification of the coatings by changing the methodology from DC to HiPIMS was not observed.
October, 2020 | DOI: 10.1016/j.matlet.2020.128334
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Microstructure and thermal conductivity of Si-Al-C-O fiber bonded ceramics joined to refractory metals
Vera, MC; Martinez-Fernandez, J; Singh, M; Casalegno, V; Balagna, C; Ramirez-Rico, JMaterials Letters, 276 (2020) 128203
Show abstract ▽
We explore joining Si-Al-C-O fiber-bonded ceramics to Cu-clad-Mo using an Ag-Ti-Cu brazing alloy. A temperature of 900 degrees C and times in the range of 10-20 min are required to obtain sound joints irrespectively of the fiber orientation. The reaction layer is 1-2 mu m thick and free of pores and defects. The thermal conductivity of the joined samples is well described considering that the metal and the ceramic are in series for thermal resistance. This implies that the joint is highly conductive and forms an almost perfect
October, 2020 | DOI: 10.1016/j.matlet.2020.128203
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Elucidating esterification reaction during deposition of cutin monomers from classical molecular dynamics simulations
Bueno, OVM; Benitez, JJ; San-Miguel, MAJournal of Molecular Modeling, 26 (2020) 280
Show abstract ▽
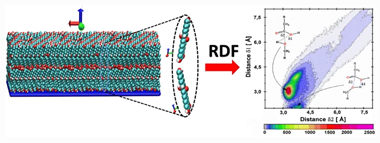
The structural behavior of some cutin monomers, when deposited on mica support, was extensively investigated by our research group. However, other events, such as esterification reaction (ER), are still a way to explore. In this paper, we explore possible ER that could occur when these monomers adsorb on support. Although classical molecular dynamics simulations are not able to capture reactive effects, here, we show that they become valuable strategies to analyze the initial structural configurations to predict the most favorable reaction routes. Thus, when depositing aleuritic acid (ALE), it is observed that the loss of capacity to form self-assembled (SA) systems favors different routes to occur ER. In pure ALE bilayers systems, an ER is given exclusively through the -COOH and primary -OH groups. In pure ALE monolayers systems, the ER does not happen when the system is self-assembled. However, for disorganized systems, it is able to occur by two possible routes: -COOH and primary -OH (route 1) and -COOH and secondary -OH (route 2). When palmitic acid (PAL) is added in small quantities, ALE SAMs can now form an ER. In this case, ER occurs mostly through the -COOH and secondary -OH groups. However, when the presence of PAL is dominant, ER can occur with either of both possibilities, that is, routes 1 and 2.
September, 2020 | DOI: 10.1007/s00894-020-04544-9
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Bimetallic PdAu catalysts for formic acid dehydrogenation
Santos, JL; Leon, C; Monnier, G; Ivanova, S; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAInternational Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 45 (2020) 23056-23068
Show abstract ▽
A series of monometallic and bimetallic palladium gold catalyst were prepared and studied for the formic acid dehydrogenation reaction. Different Pd/Au compositions were employed (PdxAu100-x, where x = 25; 50 and 75) and their impact on alloy structure, particle size and dispersion was evaluated. Active phase composition and reaction parameters such as temperature, formic acid concentration or formate/formic acid ratio were adjusted to obtain active and selective catalyst for hydrogen production. An important particle size effect was observed and related to Pd/Au composition for all bimetallic catalysts.
September, 2020 | DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2020.06.076
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Free-Carbon Surface for PtCu Nanoparticles: An In Situ Near Ambient Pressure X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy Study
Castillo, R; Navarro-Jaen, S; Romero-Sarria, F; Perez-Dieste, V; Escudero, C; Centeno, MA; Daturi, M; Odriozola, JAJournal of Physical Chemistry C, 124 (2020) 19046-19056
Show abstract ▽
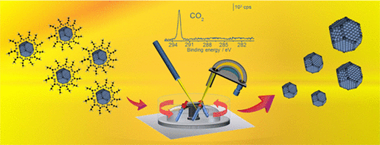
Usually, nanoparticle synthesis methodologies require the use of organic molecules (capping agent, solvent molecules, etc.), which results in carbon deposits on the nanoparticle surface. These residues modify the surface properties mainly affecting the catalytic behavior. In this work, unsupported poly(vinylpyrrolidone) (PVP)-stabilized PtCu (1:3 molar ratio) bimetallic alloy nanoparticles were synthetized and characterized. An alternative surface cleaning method has been designed, which successfully removes the presence of organic fragments. To address this key issue, we have combined a first nanoparticle washing step with a near ambient pressure X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (NAPXPS) study in order to obtain a clean active site and the total understanding of the carbon elimination mechanism. The dynamic evolution of the surface organic species composition under different gas mixtures at 750 mTorr and 350 degrees C has been studied, and only under CO2 exposure, NAPXPS analysis revealed a total availability of the active site by the removal of the organic nanoparticle coating.
September, 2020 | DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.0c04713
- ‹ previous
- 93 of 410
- next ›














