Scientific Papers in SCI
2020
2020
Materiales Avanzados
Characterization, thermal and ceramic properties of phyllite clays from southeast Spain
Garzon, Eduardo; Perez-Villarejo, Luis; Sanchez-Soto, Pedro J.Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 142 (2020) 1659-1670
Show abstract ▽
The present research studied a set of phyllite clays from several deposits in southeast Spain. These phyllite clays have traditionally been used as sealing material to impermeabilize roofs, embankments, ponds, construction and waste landfill, with recent applications in the preparation of new mortars. However, studies on thermal behaviour and ceramic properties of phyllite clays have been scarce. The present research showed a summary of previous characterization studies on representative phyllite clays from these deposits with additional results. Mineralogical, by X-ray diffraction, and chemical, by X-ray fluorescence characterization of these samples were summarized. Thermal analysis methods (DTA-TG and thermal diffractometry) were applied to achieve a more complete mineralogical characterization. Several phyllite clay samples were selected for a ceramic study by firing pressed powdered samples up to 1300 degrees C. Sintered or vitrified materials, with porosities almost zero, were obtained from these phyllite clays after firing at 1100-1200 degrees C, with apparent densities between 2.1 and 2.4 g cm(-3). Higher firing temperatures (> 1250 degrees C) produced deformation and expansion of the ceramic bodies. These results allowed obtain the vitrification temperature (T-v) and the temperature of the maximum bulk density (T-d). According to the previous mineralogical and chemical characterization and the values of these parameters, the phyllite clay samples were classified in three varieties, as follows: (1)Micaceous, characterized by predominant layer silicates, mainly muscovite or illite, alkaline elements (mainly K2O higher than 3.5 mass%) and lower values of both T(v)and T-d, (2)Quartzitic, with predominant quartz and SiO(2)and intermediate values of T(v)and T-d, and (3)Carbonaceous, characterized by predominant dolomite, medium contents of CaO and MgO and higher values of both T(v)and T-d. These results are interesting for the application of these phyllite clays as ceramic raw materials.
December, 2020 | DOI: 10.1007/s10973-020-10160-9
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Robust anti-icing superhydrophobic aluminum alloy surfaces by grafting fluorocarbon molecular chains
Rico, V; Mora, J; Garcia, P; Aguero, A; Borras, A; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Lopez-Santos, CApplied Materials Today, 21 (2020) 100815
Show abstract ▽
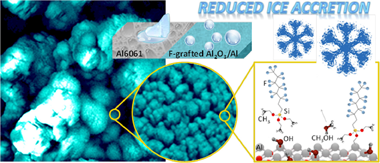
Infusion of low surface tension liquids in nanostructured surfaces is currently used to promote an anti icing response, although the long term stability of these systems is often jeopardized by losses of the infused liquid. In this work, we propose an alternative to the infusion procedure to induce a more effective and long lasting anti-icing capacity. The method consists of a combination of surface nanostructuration with the chemical grafting of fluorocarbon molecules. Al6061 substrates have been subjected to laser roughening and further modified with a nanostructured Al2O3 thin film to achieve a dual roughness and porous surface state. These surfaces have been subjected to a grafting treatment with perfluorooctyltriethoxysilane (PFOTES) vapor or, for comparative purposes, infused with a low surface tension liquid. A comparative analysis of the wetting, water condensation and anti-icing properties of these two systems showed an outstandingly better performance for the grafted surfaces with respect to the infused ones. Grafted surfaces were markedly superhydrophobic and required higher water vapor pressures to induce condensation. When looking for their anti-icing capacity, they presented quite long freezing delay times for supercooled water droplets (i.e. almost four hours) and exhibited a notably low ice accretion in a wind tunnel test. The high aging resistance and durability of these grafted surfaces and the reproducibility of the results obtained when subjected to successive ice accretion cycles show that molecular grafting is an efficient anti-icing methodology that, in aggressive media, may outperform the classical infusion procedures. The role of the fluorocarbon chains anchored on the surface in inducing an anti-icing functionality is discussed.
December, 2020 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apmt.2020.100815
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
(NH4)4[NiMo6O24H6].5H2O / g-C3N4 materials for selective photo-oxidation of Csingle bondO and Cdouble bondC bonds
Caudillo-Flores, U; Ansari, F; Bachiller-Baeza, B; Colon, G; Fernandez-Garcia, M; Kubacka, AApplied Catalysis B-Environmental, 278 (2020) 119299
Show abstract ▽
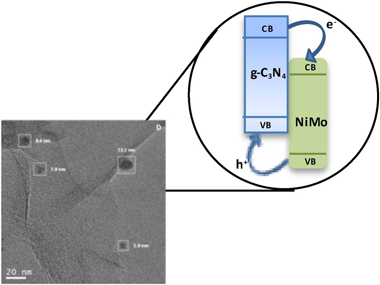
Novel composite photo-catalysts having (NH4)(4)[NiMo6O24H6]center dot 5H(2)O Polyoxometalate (POM) species deposited over g-C3N4 are synthesized. Materials were characterized through a multitechnique approach showing the stability of the carbon nitride component both through the synthesis process and under reaction. Contrarily, the POM component evolves under reaction conditions to maximize the interaction with the support. Such a behavior renders, as measured by the quantum efficiency, highly active photo-catalysts in the photo-oxidation of 2-propanol and styrene both under UV and sunlight illumination, setting up the basis for a green catalytic process. The material having a 4 wt. % POM showed improved activity with respect to both parent constituents but also higher selectivity to the partial oxidation of the alcohol and the aromatic hydrocarbon to generate added value chemical compounds. A multitechnique approach investigating charge carrier fate demonstrates the key role played by the interaction between components to promote activity and selectivity in selective oxidation reactions.
December, 2020 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2020.119299
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Influence of Water on the Oxidation of NO on Pd/TiO2 Photocatalysts
M.J. Hernández Rodríguez; E. Pulido Melián; J. Araña; J.A. Navío; O.M. González Díaz; Dunia E. Santiago; J.M. Doña RodríguezNanomaterials, 10 (2020) 2354
Show abstract ▽
Two series of new photocatalysts were synthesized based on modification with Pd of the commercial P25 photocatalyst (EVONIK®). Two techniques were employed to incorporate Pd nanoparticles on the P25 surface: photodeposition (series Pd-P) and impregnation (series Pd-I). Both series were characterized in depth using a variety of instrumental techniques: BET, DRS, XRD, XPS, TEM, FTIR and FESEM. The modified series exhibited a significant change in pore size distribution, but no differences compared to the original P25 with respect to crystalline phase ratio or particle size were observed. The Pd0 oxidation state was predominant in the Pd-P series, while the presence of the Pd2+ oxidation state was additionally observed in the Pd-I series. The photoactivity tests were performed in a continuous photoreactor with the photocatalysts deposited, by dip-coating, on borosilicate glass plates. A total of 500 ppb of NO was used as input flow at a volumetric flow rate of 1.2 L·min−1, and different relative humidities from 0 to 65% were tested. The results obtained show that under UV-vis or Vis radiation, the presence of Pd nanoparticles favors NO removal independently of the Pd incorporation method employed and independently of the tested relative humidity conditions. This improvement seems to be related to the different interaction of the water with the surface of the photocatalysts in the presence or absence of Pd. It was found in the catalyst without Pd that disproportionation of NO2 is favored through its reaction with water, with faster surface saturation. In contrast, in the catalysts with Pd, disproportionation took place through nitro-chelates and adsorbed NO2 formed from the photocatalytic oxidation of the NO. This different mechanism explains the greater efficiency in NOx removal in the catalysts with Pd. Comparing the two series of catalysts with Pd, Pd-P and Pd-I, greater activity of the Pd-P series was observed under both UV-vis and Vis radiation. It was shown that the Pd0 oxidation state is responsible for this greater activity as the Pd-I series improves its activity in successive cycles due to a reduction in Pd2+ species during the photoactivity tests.
December, 2020 | DOI: 10.3390/nano10122354
Reactividad de Sólidos
Control of experimental conditions in reaction flash-sintering of complex stoichiometry ceramics
Gil-Gonzalez, E; Perejon, A; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Roman-Gonzalez, D; Perez-Maqueda, LACeramics International, 46 (2020) 29413-29420
Show abstract ▽
The inherent potential of reaction flash-sintering for the preparation of complex oxides is evidenced by the one-step synthesis and densification of a ceramic of complex stoichiometry. The system Bi0.93La0.07FeO3, a multi-ferroic ceramic with promising technological applications, has been chosen. This system presents three different metals in its composition and it is extremely challenging to prepare by conventional procedures. Non-stoichiometric materials with unwilling secondary phases are usually obtained by conventional methods, due to the high volatility of bismuth oxide at the temperatures required for inducing the solid-solid reactions. Here, it is demonstrated that a careful control of the experimental flash conditions (applied electric field and selected current density limit) is required to obtain a high quality ceramic. Small deviations from the optimum conditions result in either non-stoichometric or poorly densified samples.
December, 2020 | DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.05.091
- ‹ previous
- 89 of 410
- next ›














