Scientific Papers in SCI
2021
2021
Materiales Coloidales
Dysprosium and Holmium Vanadate Nanoprobes as High-Performance Contrast Agents for High-Field Magnetic Resonance and Computed Tomography Imaging
Gomez-Gonzalez, E; Nunez, NO; Caro, C; Garcia-Martin, ML; Fernandez-Afonso, Y; de la Fuente, JM; Balcerzyk, M; Ocana, MInorganic Chemistry, 60 (2021) 152-160
Show abstract ▽
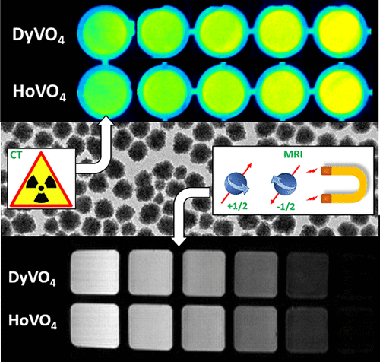
We describe a wet chemical method for the synthesis of uniform and well-dispersed dysprosium vanadate (DyVO4) and holmium vanadate (HoVO4) nanoparticles with an almost spherical shape and a mean size of ∼60 nm and their functionalization with poly(acrylic acid). The transverse magnetic relaxivity of both systems at 9.4 T is analyzed on the basis of magnetic susceptibility and magnetization measurements in order to evaluate their potential for application as high-field MRI contrast agents. In addition, the X-ray attenuation properties of these systems are also studied to determine their capabilities as computed tomography contrast agent. Finally, the colloidal stability under physiological pH conditions and the cytotoxicity of the functionalized NPs are also addressed to assess their suitability for bioimaging applications.
January, 2021 | DOI: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.0c02601
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Enhanced Directional Light Extraction from Patterned Rare-Earth Phosphor Films
Cabello-Olmo, E; Molet, P; Mihi, A; Lozano, G; Miguez, HAdvanced Optical Materials, 9 (2021) 2001611
Show abstract ▽
The combination of light‐emitting diodes (LEDs) and rare earth (RE) phosphors as color‐converting layers comprises the basis of solid‐state lighting. Indeed, most LED lamps include a photoluminescent coating made of phosphor material, i.e., crystalline matrix suitably doped with RE elements, to produce white light from a blue or ultraviolet LED chip. Transparent phosphor‐based films constitute starting materials for new refined emitters that allow different photonic designs to be implemented. Among the different photonic strategies typically employed to tune or enhance emission, surface texturing has proved its versatility and feasibility in a wide range of materials and devices. However, most of the nanofabrication techniques cannot be applied to RE phosphors directly because of their chemical stability or because of their cost. The first monolithic patterned structure of down‐shifting nanophosphors with square arrays of nanoholes with different lattice parameters is reported in this study. It is shown that a low‐cost soft‐nanolithography procedure can be applied to red‐emitting nanophosphors (GdVO4:Eu3+ nanocrystals) to tune their emission properties, attaining a twofold directional enhancement of the emitted light at predesigned emission wavelengths in specific directions.
January, 2021 | DOI: 10.1002/adom.202001611
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Disentangling Electron–Phonon Coupling and Thermal Expansion Effects in the Band Gap Renormalization of Perovskite Nanocrystals
Rubino, A; Francisco-Lóprez, A.; Baker, A.J., Petrozza, A.; Calvo, M.E.; Goñi, A.R.; Míguez, H.Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 12 (2021) 569-575
Show abstract ▽
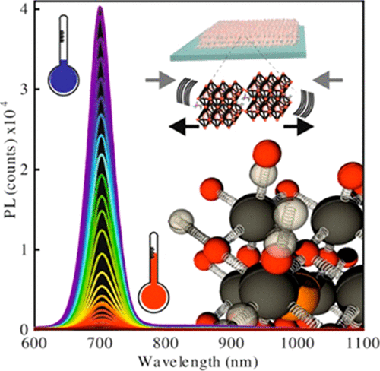
The complex electron–phonon interaction occurring in bulk lead halide perovskites gives rise to anomalous temperature dependences, like the widening of the electronic band gap as temperature increases. However, possible confinement effects on the electron–phonon coupling in the nanocrystalline version of these materials remain unexplored. Herein, we study the temperature (ranging from 80 K to ambient) and hydrostatic pressure (from atmospheric to 0.6 GPa) dependence of the photoluminescence of ligand-free methylammonium lead triiodide nanocrystals with controlled sizes embedded in a porous silica matrix. This analysis allowed us to disentangle the effects of thermal expansion and electron–phonon interaction. As the crystallite size decreases, the electron–phonon contribution to the gap renormalization gains in importance. We provide a plausible explanation for this observation in terms of quantum confinement effects, showing that neither thermal expansion nor electron–phonon coupling effects may be disregarded when analyzing the temperature dependence of the optoelectronic properties of perovskite lead halide nanocrystals.
January, 2021 | DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.0c03042
Reactividad de Sólidos
Critical Influence of the Processing Route on the Mechanical Properties of Zirconia Composites with Graphene Nanoplatelets
Gallardo-Lopez, A; Munoz-Ferreiro, C; Lopez-Pernia, C; Jimenez-Pique, E; Gutierrez-Mora, F; Morales-Rodriguez, A; Poyato, RMaterials, 14 (2021) 108
Show abstract ▽
Graphene-based nanostructures, used as potential reinforcement in ceramic composites, have a great tendency to agglomerate. This requires the use of homogenization techniques during the powder processing, posing the need to evaluate how these techniques affect the microstructure and the mechanical properties of the resulting composites. The influence of the processing route on the properties of 3YTZP (3 mol % yttria tetragonal zirconia polycrystals) ceramic composites with 10 vol % cost-effective GNP (graphene nanoplatelets) has been addressed. Four different powder processing routines combining ultrasonic powder agitation (UA) and planetary ball milling (PBM) in wet and dry media have been used and all the composites were densified by spark plasma sintering (SPS). The mechanical properties at room temperature in the macroscale have been assessed by Vickers indentations, four-point bending tests and the impulse-echo technique, while instrumented indentation was used to measure the hardness and Young’s modulus at the nanoscale. The application of dry-PBM enhances greatly the mechanical and electrical isotropy of the composites, slightly increases the hardness and lowers the elastic modulus, independently of the application of UA. The combination of UA and dry-PBM enhances the flexure strength by 50%, which is desirable for structural applications.
January, 2021 | DOI: 10.3390/ma14010108
2020
2020
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Efficient third harmonic generation from FAPbBr(3) perovskite nanocrystals
Rubino, A; Huq, T; Dranczewski, J; Lozano, G; Calvo, ME; Vezzoli, S; Miguez, H; Sapienza, RJournal of Materials Chemistry C, 8 (2020) 15990-15995
Show abstract ▽
The development of versatile nanostructured materials with enhanced nonlinear optical properties is relevant for integrated and energy efficient photonics. In this work, we report third harmonic generation from organic lead halide perovskite nanocrystals, and more specifically from formamidinium lead bromide nanocrystals, ncFAPbBr(3), dispersed in an optically transparent silica film. Efficient third order conversion is attained for excitation in a wide spectral range in the near infrared (1425 nm to 1650 nm). The maximum absolute value of the modulus of the third order nonlinear susceptibility of ncFAPbBr(3), chi((3)NC), is derived from modelling both the linear and nonlinear behaviour of the film and is found to be chi((3)NC) = 1.46 x 10(-19) m(2) V-2 (or 1.04 x 10(-11) esu) at 1560 nm excitation wavelength, which is of the same order as the highest previously reported for purely inorganic lead halide perovskite nanocrystals (3.78 x 10(-11) esu for ncCsPbBr(3)). Comparison with the experimentally determined optical constants demonstrates that maximum nonlinear conversion is attained at the excitonic resonance of the perovskite nanocrystals where the electron density of states is largest. The ease of synthesis, the robustness and the stability provided by the matrix make this material platform attractive for integrated nonlinear devices.
December, 2020 | DOI: 10.1039/d0tc04790b
- ‹ previous
- 88 of 410
- next ›














