Scientific Papers in SCI
2021
2021
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Overcoming Pd-TiO2 Deactivation during H-2 Production from Photoreforming Using Cu@Pd Nanoparticles Supported on TiO2
Platero, F; Lopez-Martin, A; Caballero, A; Rojas, TC; Nolan, M; Colon, GACS Applied Nano Materials, 4 (2021) 3204-3219
Show abstract ▽
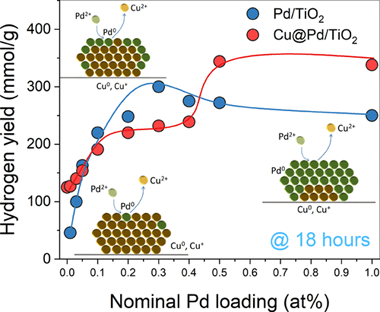
Different Cu@Pd-TiO2 systems have been prepared by a two-step synthesis to obtain a bimetallic co-catalyst for the H-2 photoreforming reaction. We find that the tailored deposition of Pd covering the Cu nanoclusters by a galvanic replacement process results in the formation of a core@shell structure. The photocatalytic H-2 production after 18 h is 350 mmol/g on the Cu@Pd-1.0-TiO2 bimetallic system, which is higher than that on the monometallic ones with a H-2 production of 250 mmol/g on Pd-supported TiO2. Surface characterization by highangle annular dark-field scanning transmission electron microscopy, H-2-temperatureprogramed reduction, CO-FTIR spectroscopy, and XPS gives clear evidence of the formation of a core@shell structure. With a Pd loading of 0.2-0.3 at. %, we propose a full coverage of the Cu nanoparticles with Pd. Long-time photoreforming runs show the enhanced performance of supported Cu@Pd with respect to bare palladium leading to a more stable catalyst and ultimately higher H-2 production.
March, 2021 | DOI: 10.1021/acsanm.1c00345
Reactividad de Sólidos
A first insight into the microstructure and crack propagation in novel boron nitride nanosheet/3YTZP composites
Munoz-Ferreiro, C; Morales-Rodriguez, A; Gallardo-Lopez, A; Poyato, RBoletin de la Sociedad Española de Cerámica y Vidrio, 60 (2021) 128-136
Show abstract ▽
In this work, novel 3 mol% yttria tetragonal zirconia polycristalline (3YTZP) ceramic composites with boron nitride nanosheets (BNNS) are investigated for the first time. Highly densified composites with 1 and 4 vol% BNNS were obtained by spark plasma sintering (SPS) after BNNS synthesis using a solution exfoliation method and BNNS dispersion into the ceramic powder by ultrasonication. The BNNS presented homogeneous distribution throughout the ceramic matrix and preferential alignment in the plane perpendicular to the pressing axis during SPS. The BNNS incorporation had practically no effect on the Vickers hardness of the material nor on the Young's modulus. Anisotropy in crack development was found in the composite with 4% vol BNNS, together with a mechanism of extensive microcracking. Several energy-absorbing mechanisms during crack propagation, such as crack deflection, crack bridging, crack branching, BNNS pull-out and BNNS debonding, were identified in the composites by a close observation of the indentation-induced fracture paths.
March, 2021 | DOI: 10.1016/j.bsecv.2020.02.003
Reactividad de Sólidos
EGFR-targeting antitumor therapy: Neuregulins or antibodies?
de Lavera, I; Merkling, PJ; Oliva, JM; Sayagues, MJ; Cotan, D; Sanchez-Alcazar, JA; Infante, JJ; Zaderenko, A.P.European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 158 (2021) 105678
Show abstract ▽
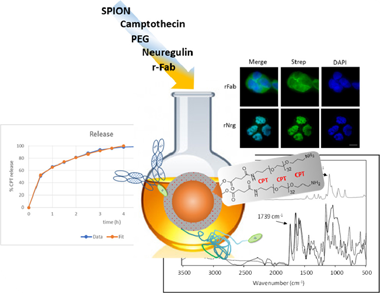
Malignancies such as lung, breast and pancreatic carcinomas are associated with increased expression of the epidermal growth factor receptor, EGFR, and its role in the pathogenesis and progression of tumors has made this receptor a prime target in the development of antitumor therapies. In therapies targeting EGFR, the development of resistance owing to mutations and single nucleotide polymorphisms, and the expression of the receptor ligands themselves are very serious issues. In this work, both the ligand neuregulin and a bispecific antibody fragment to EGFR are conjugated separately or together to the same drug-delivery system to find the most promising candidate. Camptothecin is used as a model chemotherapeutic drug and superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles as a delivery system. Results show that the lowest LD50 is achieved by formulations conjugated to both the antibody and the ligand, demonstrating a synergy. Additionally, the ligand location in the nucleus favors the antitumor activity of Camptothecin. The high loading capacity and efficiency convert these systems into a good alternative for administering Camptothecin, a drug whose use is otherwise severely limited by its chemical instability and poor solubility. Our choice of targeting agents allows treating tumors that express ErbB2 (Her2+ tumors) as well as Her2- tumors expressing EGFR.
March, 2021 | DOI: 10.1016/j.ejps.2020.105678
Propiedades mecánicas, modelización y caracterización de cerámicos avanzados
Cation-driven electrical conductivity in Ta-doped orthorhombic zirconia ceramics
Moshtaghioun, BM; Laguna-Bercero, MA; Pena, JI; Gomez-Garcia, D; Dominguez-Rodriguez, ACeramics International, 47 (2021) 7248-7522
Show abstract ▽
This paper is devoted to the study of the electrical conductivity of tantalum-doped zirconia ceramics prepared by spark plasma sintering. In this study, the temperature dependence of conductivity in as-prepared specimens and in those previously annealed in air is determined and compared. A semi-empirical model, which is based on the oxidation states of the cations, has been developed and successfully assessed. According to this, the conductivity is basically controlled by the diffusion of tetravalent zirconium cations in both cases, although the concentration of these species varies drastically with the amount of induced oxygen vacancies. This is a quite unexpected fact, since conductivity is normally controlled by anionic diffusion in zirconia ceramics. This option is forbidden here due to the presence of substitutional pentavalent cations. Therefore, conductivity values are much lower than those reported in trivalent or divalent substitutional cation doped zirconia ceramics.
March, 2021 | DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.10.227
Materiales para Bioingeniería y Regeneración Tisular
Nanofibrous Gelatin-Based Biomaterial with Improved Biomimicry Using D-Periodic Self-Assembled Atelocollagen
Borrego-Gonzalez, S; Dalby, MJ; Diaz-Cuenca, ABiomimetics, 6 (2001) 20
Show abstract ▽
Design of bioinspired materials that mimic the extracellular matrix (ECM) at the nanoscale is a challenge in tissue engineering. While nanofibrillar gelatin materials mimic chemical composition and nano-architecture of natural ECM collagen components, it lacks the characteristic D-staggered array (D-periodicity) of 67 nm, which is an important cue in terms of cell recognition and adhesion properties. In this study, a nanofibrous gelatin matrix with improved biomimicry is achieved using a formulation including a minimal content of D-periodic self-assembled atelocollagen. We suggest a processing route approach consisting of the thermally induced phase separation of the gelatin based biopolymeric mixture precursor followed by chemical-free material cross-linking. The matrix nanostructure is characterized using field emission gun scanning electron microscopy (FEG-SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), wide angle X-ray diffraction (XRD) and Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR). The cell culture assays indicate that incorporation of 2.6 wt.% content of D-periodic atelocollagen to the gelatin material, produces a significant increase of MC3T3-E1 mouse preosteoblast cells attachment and human mesenchymal stem cells (hMSCs) proliferation, in comparison with related bare gelatin matrices. The presented results demonstrate the achievement of an efficient route to produce a cost-effective, compositionally defined and low immunogenic “collagen-like” instructive biomaterial, based on gelatin.
March, 2021 | DOI: 10.3390/biomimetics6010020
- ‹ previous
- 83 of 410
- next ›














