Scientific Papers in SCI
2021
2021
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Electrochromic response and porous structure of WO3 cathode layers
Louloudakis, D; Mouratis, K; Gil-Rostra, J; Koudoumas, E; Alvarez, R; Palmero, A; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARElectrochimica Acta, 376 (2021) 138049
Show abstract ▽
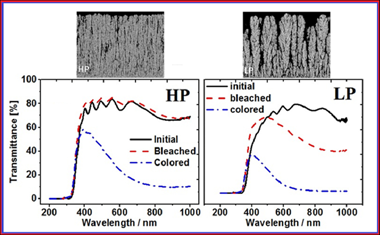
Maximizing the electrochromic response of tungsten oxide-based systems demands highly porous electrode layers that facilitate the incorporation of electrolyte cations during the reduction process. In this work, amorphous and porous WO3 thin films were grown on indium tin dioxide glass substrates by magnetron sputtering at oblique angles at two different plasma gas pressures. Remarkably, the film that showed higher porosity presented a worse electrochromic response in terms of durability, time response and charge density capacity. This result is analyzed and explained on the basis of the features of the porous structure of the films: While the typical nanostructure developed at low pressures possesses large and connected pore voids with few ramifications, the nanostructure generated at a higher pressure presents a rather sponge-like porous structure with numerous and small well-connected voids. A general discussion on the role of the porous structure and, particularly, on the accessible pore volume and area is carried out. It is concluded that not only the accessible pore volume, defining the volume of electrolyte that stays inside the layer, but also the accessible pore area, which defines the efficiency of the incorporation/release of Li+ cations within the electrode material, determine the efficiency and reversibility of the electrochromic response.
April, 2021 | DOI: 10.1016/j.electacta.2021.138049
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Cu supported Fe-SiO2 nanocomposites for reverse water gas shift reaction
Gonzalez-Castano, M; de Miguel, JCN; Sinha, F; Wabo, SG; Klepel, O; Arellano-Garcia, HJournal of CO2 Utilization, 46 (2021) 101493
Show abstract ▽
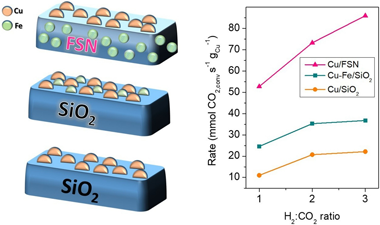
This work analyses the catalytic activity displayed by Cu/SiO2, Cu-Fe/SiO2 and Cu/FSN (Fe-SiO2 nanocomposite) catalysts for the Reverse Water Gas Shift reaction. Compared to Cu/SiO2 catalyst, the presence of Fe resulted on higher CO?s selectivity and boosted resistances against the constitution of the deactivation carbonaceous species. Regarding the catalytic performance however, the extent of improvement attained through incorporation Fe species strongly relied on the catalysts' configuration. At 30 L/gh and H-2:CO2 ratios = 3, the performance of the catalysts? series increased according to the sequence: Cu/SiO2 < Cu-Fe/SiO2 << Cu/FSN. The remarkable catalytic enhancements provided by Fe-SiO2 nanocomposites under different RWGS reaction atmospheres were associated to enhanced catalyst surface basicity's and stronger Cu-support interactions. The catalytic promotion achieved by Fe-SiO2 nanocomposites argue an optimistic prospective for nanocomposite catalysts within future CO2-valorising technologies.
April, 2021 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jcou.2021.101493
Materiales para Bioingeniería y Regeneración Tisular
Nanofibrous Matrix of Defined Composition Sustains Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell Culture
Borrego-Gonzalez, S; de la Cerda, B; Diaz-Corrales, FJ; Diaz-Cuenca, AACS Applied Bio Materials, 4 (2021) 3035-3040
Show abstract ▽
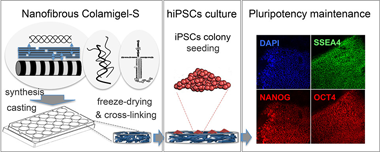
Human induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSCs) represent the most promising biological material for regenerative medicine applications. In this work, a 3D solid nanofibrous matrix of defined composition (Colamigel-S) consisting of 97 wt % gelatin, 2.6 wt % atelocollagen, and 0.4 wt % laminin has been reproducibly processed and characterized and exhibits a homogeneous nanofibrillar network of high surface area, interconnected microcavities, and typical D-periodic collagen fibril nanostructural features. The purpose of the study was to test the performance of Colamigel-S as substrate for in vitro hiPSCs culture, finding that these cells efficiently attach and grow keeping their characteristic stem morphology and undifferentiated state.
April, 2021 | DOI: 10.1021/acsabm.0c00425
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Zr and Fe on Pt/CeO2-MOx/Al2O3 catalysts for WGS reaction
Gonzalez-Castano, M; Ivanova, S; Centeno, MA; Ioanides, T; Arellano-Garcia, H; Odriozola, JAInternational Journal of Hydrogen Energy, (2021)
Show abstract ▽
By evaluating the functional modifications induced by Zr and Fe as dopants in Pt/CeO2‐MOx/Al2O3 catalysts (M = Fe and Zr), the key features for improving water gas shift (WGS) performance for these systems have been addressed. Pt/ceria intrinsic WGS activity is often related to improved H2 surface dynamics, H2O absorption, retentions and dissociation capacities which are influenced greatly by the support nature. Two metals, iron and zirconia, were chosen as ceria dopants in this work, either in separate manner or combined. Iron incorporation resulted in CO‐redox properties and oxygen storage capacities (OSC) improvement but the formation of Ce‐Fe solid solutions did not offer any catalytic benefit, while the Zr incorporation influenced in a great manner surface electron densities and shows higher catalytic activity. When combined both metals showed an important synergy evidenced by 30% higher CO conversions and attributed to greater surface electron densities population and therefore absorption and activity. This work demonstrates that for Pt/ceria catalysts OSC enhancement does not necessarily imply a catalytic promotion.
March, 2021 | DOI: 10.1002/er.6646
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Facile synthesis and characterization of a novel 1,2,4,5-benzene tetracarboxylic acid doped polyaniline@zinc phosphate nanocomposite for highly efficient removal of hazardous hexavalent chromium ions from water
Abdelghani Hsini, Yassine Naciri, Mohamed Benafqir, Zeeshan Ajmal, Nouh Aarab, Mohamed Laabd, J.A. Navío, F. Puga, Rabah Boukherroub, Bahcine Bakiz, Abdallah AlbourineJournal of Colloid and Interface Science, 585 (2021) 560-573
Show abstract ▽
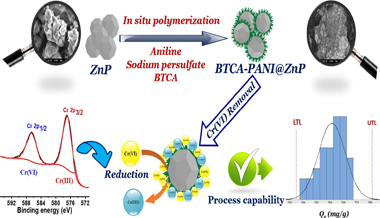
The present study describes the preparation of a novel 1,2,4,5-benzene tetracarboxylic acid doped polyaniline@zinc phosphate (BTCA-PANI@ZnP) nanocomposite via a facile two-step procedure. Thereafter, the as-prepared composite material adsorption characteristics for Cr(VI) ions removal were evaluated under batch adsorption. Kinetic approach studies for Cr(VI) removal, clearly demonstrated that the results of the adsorption process followed the pseudo second order and Langmuir models. The thermodynamic study indicated a spontaneous and endothermic process. Furthermore, higher monolayer adsorption was determined to be 933.88 mg g1 . In addition, the capability study regarding Cr(VI) ions adsorption over BTCA-PANI@ZnP nanocomposite clearly revealed that our method is suitable for large scale application. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) analysis confirmed Cr(VI) adsorption on the BTCA-PANI@ZnP surface, followed by its subsequent reduction to Cr(III). Thus, the occurrence of external mass transfer, electrostatic attraction and reduction phenomenon were considered as main mechanistic pathways of Cr(VI) ions removal. The superior adsorption performance of the material, the multidimensional characteristics of the surface and the involvement of multiple removal mechanisms clearly demonstrated the potential applicability of the BTCA-PANI@ZnP material as an effective alternative for the removal of Cr(VI) ions from wastewater.
March, 2021 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jcis.2020.10.036
- ‹ previous
- 81 of 410
- next ›














