Scientific Papers in SCI
2023
2023
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
H2 Production from NH3 in a BaTiO3 Moderated Ferroelectric Packed-Bed Plasma Reactor
Ruiz-Martín, M; Marin-Meana, S; Megías-Sánchez, A; Oliva-Ramírez, M; Cotrino, J; González-Elipe, AR; Gómez-Ramírez, AP.asma Chemistry and Plasma Processing, 43 (2023) 2093-2110
Show abstract ▽
Plasma decomposition reactions are used for various gas phase chemical processes including the decomposition of ammonia. In this work we show that pure ammonia can be effectively decomposed at atmospheric pressure and ambient temperature using a packed-bed plasma reactor moderated with BaTiO3 ferroelectric pellets without catalyst. The decomposition rate and energy efficiency of this ferroelectric barrier discharge reactor have been monitored as a function of applied voltage (up to a maximum value of 2.5 kV) and flow rate. For each operating condition reaction efficiencies have been correlated with the parameters defining the electrical response of the reactor. It is found that plasma current and volume inside the reactor and hence the energy efficiency of the process and the decomposition rate vary with the applied voltage and the flow of ammonia (a maximum decomposition rate of 14% and an energy efficiency of 150 LH2/kWh has been determined under optimized operation conditions). The role of back reactions (i.e. N2 + 3H2 → 2NH3) in decreasing reactor performance is another key effect affecting the overall efficiency for the ammonia decomposition. The possibilities of ferroelectric barrier discharge reactors to induce the decomposition of ammonia and the importance of keeping the operating temperature below the Curie temperature of the ferroelectric material are highlighted.
November, 2023 | DOI: 10.1007/s11090-023-10427-7
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Multicomponent graphene based catalysts for guaiacol upgrading in hydrothermal conditions: Exploring "H2-free" alternatives for bio-compounds hydrodeoxygenation
Parrilla-Lahoz, S; Jin, W; Pastor-Perez, L; Duyar, MS; Martinez-Quintana, L; Dongil, AB; Reina, TRCatalysis Today, 422 (2023) 114235
Show abstract ▽
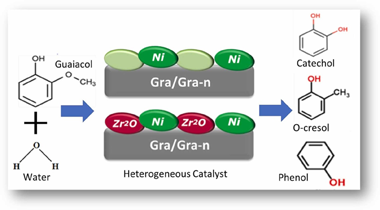
Catalytic hydrodeoxygenation (HDO) is a critical technique for upgrading biomass derivatives to deoxygenated fuels or other high-value compounds. Phenol, guaiacol, anisole, p-cresol, m-cresol and vanillin are all monomeric phenolics produced from lignin. Guaiacol is often utilised as a model lignin compound to deduce mechanistic information about the bio-oil upgrading process. Typically, a source of H2 is supplied as reactant for the HDO reaction. However, the H2 supply, due to the high cost of production and additional safety precautions needed for storage and transportation, imposes significant economic infeasibilities on the HDO process's scaling up. We investigated a novel H2-free hydrodeoxygenation (HDO) reaction of guaiacol at low temperatures and pressures, using water as both a reaction medium and hydrogen source. A variety of Ni catalysts supported on zirconia/ graphene/with/without nitrogen doping were synthesised and evaluated at 250 degrees C and 300 degrees C in a batch reactor, with the goal of performing a multi-step tandem reaction including water splitting followed by HDO. The catalysts were characterised using H2-TPR, XRD, TEM and XPS to better understand the physicochemical properties and their correlation with catalytic performance of the samples in the HDO process. Indeed, our NiZr2O/Gr-n present the best activity/selectivity balance and it is deemed as a promising catalyst to conduct the H2-free HDO reaction. The catalyst reached commendable conversion levels and selectivity to mono-oxygenated compounds considering the very challenging reaction conditions. This innovative HDO approach provides a new avenue for cost-effective biomass upgrading.
November, 2023 | DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2023.01.027
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Enhancement of upconversion photoluminescence in phosphor nanoparticle thin films using metallic nanoantennas fabricated by colloidal lithography
Ngo, TT; Viaña, JM; Romero, M; Calvo, ME; Lozano, G; Miguez, HMaterials Advances, 4 (2023) 6381-6388
Show abstract ▽
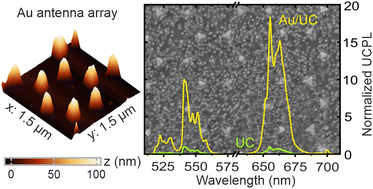
Lanthanide-doped upconversion nanoparticles (UCNPs), as multifunctional light sources, are finding utility in diverse applications ranging from biotechnology to light harvesting. However, the main challenge in realizing their full potential lies in achieving bright and efficient photon upconversion (UC). In this study, we present a novel approach to fabricate an array of gold nanoantennas arranged in a hexagonal lattice using a simple and inexpensive colloidal lithography technique, and demonstrate a significant enhancement of UC photoluminescence (UCPL) by up to 35-fold through plasmon-enhanced photoexcitation and emission. To elucidate the underlying physical mechanisms responsible for the observed UCPL enhancement, we provide a comprehensive theoretical and experimental characterization, including a detailed photophysical description and numerical simulations of the spatial electric field distribution. Our results shed light on the fundamental principles governing the enhanced UCNPs and pave the way for their potential applications in photonic devices.
November, 2023 | DOI: 10.1039/D3MA00775H
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
A technological approach based on engineered nanoclay composites for cesium and iodine retention
Osuna, FJ; Pavon, E; Alba, MDChesmosphere, 341 (2023) 140128
Show abstract ▽
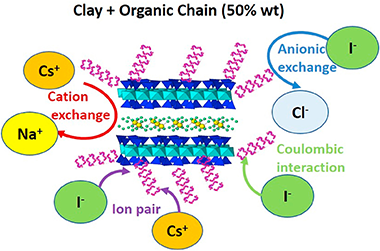
The development of effective and environmentally friendly methods for separating hazardous radionuclides from waste poses a significant technological challenge. 137Cs and 131I are among the most important radionuclides discharged into the environment by nuclear power plants. One of the best ways to eliminate them involves adsorption on clay minerals. In this regard, studies have demonstrated that organofunctionalized clay minerals are effective adsorbents. Thus, this study investigates the capability of organofunctionalized synthetic design clay minerals to jointly eliminate cesium and iodine. The adsorbents studied are a range of organofunctionalized clay minerals with alkylammonium cations of different alkyl chain lengths (2, 3 and 18) and some physical mixtures of raw clay minerals and octadecylammonium compounds. Organofunctionalized synthetic swelling highly charged micas are effective adsorbents for the simultaneous adsorption of cesium and iodine. In addition, the optimal system is a mixture of Na-M4 with octadecylammonium (50% w/w).
November, 2023 | DOI: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2023.140128
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Bismuth ferrite as innovative and efficient photocatalyst for the oxidation of As(III) to As(V) under visible light
Chianese, L; Murcia, JJ; Hidalgo, MC; Vaiano, V; Iervolino, GMaterials Science in Semiconductor Processing, 167 (2023) 107801
Show abstract ▽
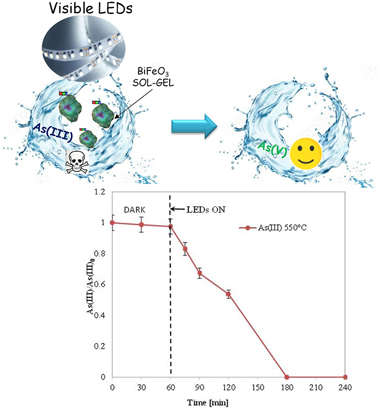
The presence of As in drinking water is a problem felt all over the world. In particular, arsenic is present in +3 (As(III)) and +5 (As(V)) oxidation states. However, As(III) is the most toxic and difficult to remove with conventional adsorption processes. A pre-oxidation process is therefore necessary. In this work, we report, for the first time, the use of BiFeO3 as a visible-light active photocatalyst for the complete and fast oxidation of As(III) to As(V) in water. In particular, the influence of annealing temperature for BiFeO3 preparation was studied and the prepared photocatalysts were characterized through XRD, N2 adsorption at −196°C, TEM, XPS, Raman and UV–Vis DRS spectroscopy. The best photocatalytic activity was achieved with BiFeO3 calcined at 550°C. The influence of catalyst dosage and the role of the main oxidizing species was evaluated, evidencing the key role of h+ in the photooxidation reaction of As(III) to As(V). Moreover, the efficiency of the photocatalyst was also evaluated in the case of drinking water contaminated by arsenic. The results demonstrated that, despite the presence of dissolved salts in the drinking water, the photocatalyst maintained its activity. The results obtained in this work prove that BiFeO3 calcined at 550°C evidenced photocatalytic performances better than different photocatalyst formulations studied for the photooxidation of As(III) to As(V) under visible light.
November, 2023 | DOI: 10.1016/j.mssp.2023.107801
- ‹ previous
- 9 of 410
- next ›














