Scientific Papers in SCI
2021
2021
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
How a small modification in the imidazolium-based SDA can determine the zeolite structure? MFI vs. TON
Megias-Sayago, C; Blanes, JMM; Szyja, BM; Odriozola, JA; Ivanova, SMicroporous and Mesoporous Materials, 322 (2021) 111160
Show abstract ▽
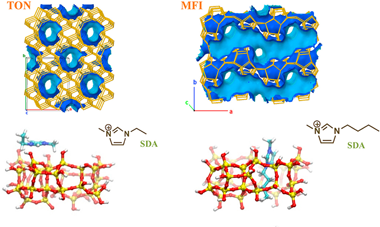
The present study proposes an important contribution to the understanding of ionic liquid role as structure directing agent for zeolite synthesis. A series of imidazolium based ionic liquids are used for this purpose. While the anionic counterpart influences the micellar organization during the synthesis, the imidazolium cation clearly directs the structure to one or another zeolite family as a function of its substituents and their interaction with the zeolite framework. The experimental observations are contrasted with molecular modeling explaining the distinct zeolite families obtained on the basis of different preferential orientation of the ionic liquids to the Si33 precursor.
July, 2021 | DOI: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2021.111160
Reactividad de Sólidos
Tuning the excitation wavelength of luminescent Mn2+-doped ZnSxSe1-x obtained by mechanically induced self-sustaining reaction
Aviles, MA; Gotor, FJOptical Materials, 117 (2021) 111121
Show abstract ▽
Mn2+-doped ZnSxSe1-x solid solution samples (Mn:ZnSxSe1-x) were synthesized by the mechanochemical process denoted as mechanically-induced self-sustaining reaction from Mn/Zn/S/Se powder elemental mixtures. The samples were characterized by X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, diffuse reflectance UV-Vis spectroscopy and emission and excitation photoluminescence measurements. The band-gap energy of samples was controlled by changing the stoichiometry, x, of the solid solution. All samples showed the characteristic Mn2+ 4T1-6A1 emission at -588 nm when exciting the host material, so it was possible to tune the excitation wavelength from 349 nm to 467 nm. However, an efficiency loss was observed with increasing Se content, probably due to the overlap between the absorption and emission spectra that induced self-absorption and emission quenching.
July, 2021 | DOI: 10.1016/j.optmat.2021.111121
Reactividad de Sólidos
Kinetic study of complex processes composed of non-independent stages: pyrolysis of natural rubber
Perejon, A; Sánchez-Jiménez, PE; García-Garrido, C; Pérez-Maqueda, LAPolymer Degradation and Stability, 188 (2021) 109590
Show abstract ▽
In this work, it is proposed a method for studying kinetics of complex processes composed of non-independent stages. In this method, the variable contribution of the different stages as a function of the heating schedule is taken into account. The method involves the simultaneous kinetic analysis of a set of experimental data registered under linear heating rate conditions, without any previous assumptions regarding the kinetic models followed by the stages or their corresponding activation energies.
The method has been tested with the kinetic analysis of the pyrolysis of natural rubber, since the kinetics of this process is complex and depends on temperature and heating schedule. It is demonstrated that the behavior of the experimental curves can be accurately predicted with the kinetic parameters calculated by the proposed methodology.
The kinetic analysis presented here could be applied to other complex processes as those found in pyrolysis, without the need of using oversimplified kinetic models that could yield significant errors when used in real applications.
June, 2021 | DOI: 10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2021.109590
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
In-situ HDO of guaiacol over nitrogen-doped activated carbon supported nickel nanoparticles
Jin, Wei; Pastor-Perez, Laura; Villora-Pico, Juan J.; Mercedes Pastor-Blas, M.; Odriozola, Jose A.; Sepulveda-Escribano, Antonio; Ramirez Reina, TomasApplied Catalysis A-General, 620 (2021) 118033
Show abstract ▽
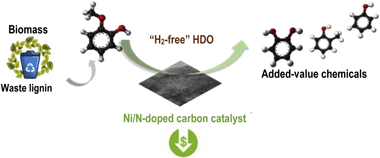
In-situ hydrodeoxygenation of guaiacol over Ni-based nitrogen-doped activated carbon supported catalysts is presented in this paper as an economically viable route for bio-resources upgrading. The overriding concept of this paper is to use water as hydrogen donor for the HDO reaction, suppressing the input of external highpressure hydrogen. The effect of nitrogen sources, including polypyrrole (PPy), polyaniline (PANI) and melamine (Mel) on the structural, electronic and ultimately of catalytic features of the designed materials have been addressed. Nitrogen-doped samples are more active than the undoped counterparts in the "H2-free" HDO process. For instance, the conversion of guaiacol increased by 8 % for Ni/PANI-AC compared to that of Ni/AC catalysts. The superior performance of Ni/NC can be attributed to the acid-base properties and modified electronic properties, which favours the C-O cleavage and water activation as well as enhances dispersion of Ni particles on the catalysts' surface.
June, 2021 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apcata.2021.118033
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
The Role of the Atmosphere on the Photophysics of Ligand-Free Lead-Halide Perovskite Nanocrystals
Moran-Pedroso, M; Rubino, A; Calvo, ME; Espinos, JP; Galisteo-Lopez, JF; Miguez, HAdvanced Optical Materials, (2021) 2100605
Show abstract ▽
Lead halide perovskite (LHP) nanocrystals (NCs) have gained attention over the past decade due to their outstanding optoelectronic properties, making them a suitable material for efficient photovoltaic and light emitting devices. Due to its soft nature, these nanostructures undergo strong structural changes upon irradiation, where these light-induced processes are strongly influenced by the environment. Since most processing routes for LHP NCs are based on colloidal approaches, the role of factors such as stabilizing ligands or solvents is usually hard to disentangle from the interaction of external radiation with the perovskite material. Employing a recently proposed synthetic approach, where ligand-free NCs can be grown within metal-oxide-based insulating nanoporous matrices, it has been feasible to perform a clean study of the effect of the surrounding atmosphere on the photophysical properties of perovskite NCs, avoiding the interference of protective capping layers or solvents. Simultaneous light-induced photo-activation and darkening processes are monitored and disentangled, and their relation with bulk and surface processes, respectively, demonstrated.
June, 2021 | DOI: 10.1002/adom.202100605
- ‹ previous
- 73 of 410
- next ›














