Scientific Papers in SCI
2022
2022
Reactividad de Sólidos
Effect of Steam Injection during Carbonation on the Multicyclic Performance of Limestone (CaCO3) under Different Calcium Looping Conditions: A Comparative Study
Troya, JJA; Moreno, V; Sánchez-Jiménez, PE; Perejon, A; Valverde, JM; Perez-Maqueda, LAACS Sustanaible Chemistry & Engineering, 10 (2022) 850-859
Show abstract ▽
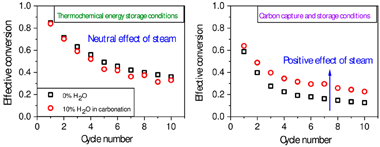
This study explores the effect of steam addition during carbonation on the multicyclic performance of limestone under calcium looping conditions compatible with (i) CO2 capture from postcombustion gases (CCS) and with (ii) thermochemical energy storage (TCES). Steam injection has been proposed to improve the CO2 uptake capacity of CaO-based sorbents when the calcination and carbonation loops are carried out in CCS conditions: at moderate carbonation temperatures (similar to 650 degrees C) under low CO2 concentration (typically similar to 15% at atmospheric pressure). However, the recent proposal of calcium-looping as a TCES system for integration into concentrated solar power (CSP) plants has aroused interest in higher carbonation temperatures (similar to 800-850 degrees C) in pure CO2. Here, we show that steam benefits the multicyclic behavior in the milder conditions required for CCS. However, at the more aggressive conditions required in TCES, steam essentially has a neutral net effect as the CO2 uptake promoted by the reduced CO2 partial pressure but also is offset by the substantial steam-promoted mineralization in the high temperature range. Finally, we also demonstrate that the carbonation rate depends exclusively on the partial pressure of CO2, regardless of the diluting gas employed.
January, 2022 | DOI: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.1c06314
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Structured and micro-structured catalysts: A fascinating future for a sustainable world – A special issue in tribute to the careers of Professors Mario Montes and José Antonio Odriozola
M.A.Centeno; L.M.Gandía; F.Romero-Sarria; O.SanzCatalysis Today, 383 (2022) 1-4
Show abstract ▽
Reactividad de Sólidos
Effect of the Processing Parameters on the Porosity and Mechanical Behavior of Titanium Samples with Bimodal Microstructure Produced via Hot Pressing
Chavez-Vasconez, R; Lascano, S; Sauceda, S; Reyes-Valenzuela, M; Salvo, C; Mangalaraja, RV; Gotor, FJ; Arevalo, C; Torres, YMaterials, 15 (2022) 136
Show abstract ▽
Commercially pure (c.p.) titanium grade IV with a bimodal microstructure is a promising material for biomedical implants. The influence of the processing parameters on the physical, microstructural, and mechanical properties was investigated. The bimodal microstructure was achieved from the blends of powder particles with different sizes, while the porous structure was obtained using the space-holder technique (50 vol.% of ammonium bicarbonate). Mechanically milled powders (10 and 20 h) were mixed in 50 wt.% or 75 wt.% with c.p. titanium. Four different mixtures of powders were precompacted via uniaxial cold pressing at 400 MPa. Then, the specimens were sintered at 750 degrees C via hot pressing in an argon gas atmosphere. The presence of a bimodal microstructure, comprised of small-grain regions separated by coarse-grain ones, was confirmed by optical and scanning electron microscopies. The samples with a bimodal microstructure exhibited an increase in the porosity compared with the commercially available pure Ti. In addition, the hardness was increased while the Young's modulus was decreased in the specimens with 75 wt.% of the milled powders (20 h).
January, 2022 | DOI: 10.3390/ma15010136
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Boosting water activation determining-step in WGS reaction on structured catalyst by Mo-doping
Garcia-Moncada, N; Jurado, L; Martinez-Tejada, LM; Romero-Sarria, F; Odriozola, JACatalysis Today, 383 (2022) 193-204
Show abstract ▽
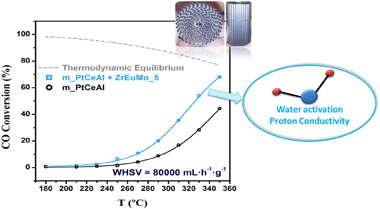
Proton conductors Mo-Eu-Zr mixed oxide systems were synthesized and further mixed with a conventional Pt/CeO2/Al2O3 catalyst to develop a highly efficient water-gas-shift (WGS) catalyst. The designed catalyst, once structured, allows reach the equilibrium conversion at medium temperatures (similar to 350 degrees C) at 80 L.g(-1) h(-1) space velocity. The ability of the proton conductor to maintain an elevated water concentration at the metal-support interface by Grotthuss' mechanism boosts the catalytic activity in WGS reaction.
The Mo-containing proton conductor is extensively characterized allowing to establish the formation of molybdenum oxide phases nucleating on top of the Eu sites in Eu-Zr oxide solid solution. [MoO4](2-) to [Mo7O24](6-) clusters nucleates at low Mo contents resulting in a alpha-MoO3 layer on increasing its content. In presence of H-2, Mobronzes are formed from similar to 200 degrees C enhancing water concentration at the surfaces and boosting the catalytic activity in the WGS reaction. These results pave the way for developing lower volume WGS reactors.
January, 2022 | DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2020.06.003
2021
2021
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
LaFeO3 Modified with Ni for Hydrogen Evolution Via Photocatalytic Glucose Reforming in Liquid Phase
G. Iervolino; V. Vaiano; D. Sannino; F. Puga; J.A. Navío; M.C. HidalgoCatalysts, 11 (2021) 1558
Show abstract ▽
In this work, the optimization of Ni amount on LaFeO3 photocatalyst was studied in the photocatalytic molecular hydrogen production from glucose aqueous solution under UV light irradiation. LaFeO3 was synthesized via solution combustion synthesis and different amount of Ni were dispersed on LaFeO3 surface through deposition method in aqueous solution and using NaBH4 as reducing agent. The prepared samples were characterized with different techniques: Raman spectroscopy, UltraViolet-Visible Diffuse Reflectance Spettroscopy (UV–Vis-DRS), X-ray Diffraction (XRD), X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS), X-ray Fluorescence (XRF), Transmission Electron microscopy (TEM), and Scanning Electron microscopy (SEM) analyses. For all the investigated photocatalysts, the presence of Ni on perovskite surface resulted in a better activity compared to pure LaFeO3. In particular, it is possible to identify an optimal amount of Ni for which it is possible to obtain the best hydrogen production. Specifically, the results showed that the optimal Ni amount was equal to nominal 0.12 wt% (0.12Ni/LaFeO3), for which the photocatalytic H2 production was equal to 2574 μmol/L after 4 h of UV irradiation. The influence of different of photocatalyst dosage and initial glucose concentration was also evaluated. The results of the optimization of operating parameters indicated that the highest molecular hydrogen production was achieved on 0.12Ni/LaFeO3 sample with 1.5 g/L of catalyst dosage and 1000 ppm initial glucose concentration. To determine the reactive species that play the most significant role in the photocatalytic hydrogen production, photocatalytic tests in the presence of different radical scavengers were performed. The results showed that •OH radical plays a significant role in the photocatalytic conversion of glucose in H2. Moreover, photocatalytic tests carried out with D2O instead of H2O evidenced the role of water molecules in the photocatalytic production of molecular hydrogen in glucose aqueous solution.
December, 2021 | DOI: 10.3390/catal11121558
- ‹ previous
- 61 of 410
- next ›














