Scientific Papers in SCI
2024
2024
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Synergistic Integration of Nanogenerators and Solar Cells: Advanced Hybrid Structures and Applications
Hajra, S; Ali, A; Panda, S; Song, HW; Rajaitha, PM; Dubal, D; Borras, A; In-Na, P; Vittayakorn, N; Vivekananthan, V; Kim, HJ; Divya, S; Oh, THAdvanced Energy Materials, (2024) 2400025
Show abstract ▽
The rapid growth of global energy consumption and the increasing demand for sustainable and renewable energy sources have urged vast research into harnessing energy from various sources. Among them, the most promising approaches are nanogenerators (NGs) and solar cells (SCs), which independently offer innovative solutions for energy harvesting. This review paper presents a comprehensive analysis of the integration of NGs and SCs, exploring advanced hybrid structures and their diverse applications. First, an overview of the principles and working mechanisms of NGs and SCs is provided for seamless hybrid integrations. Then, various design strategies are discussed, such as piezoelectric and triboelectric NGs with different types of SCs. Finally, a wide range of applications are explored that benefit from the synergistic integration of NGs and SCs, including self-powered electronics, wearable devices, environmental monitoring, and wireless sensor networks. The potential for these hybrid systems is highlighted to address real-world energy needs and contribute to developing sustainable and self-sufficient technologies. In conclusion, this review provides valuable insights into the state-of-the-art developments in NGs and SCs integration, shedding light on advanced hybrid structures and their diverse applications.
February, 2024 | DOI: 10.1002/aenm.202400025
Tribología y Protección de Superficies
Synthesis and Characterization of Multilayered CrAlN/Al2O3 Tandem Coating Using HiPIMS for Solar Selective Applications at High Temperature
Sánchez-Pérez, M; Rojas, TR; Reyes, DF; Ferrer, FJ; Farchado, M; Morales, A; Escobar-Galindo, R; Sánchez-López, JCACS Applied Energy Materials, 7 (2024) 438-449
Show abstract ▽
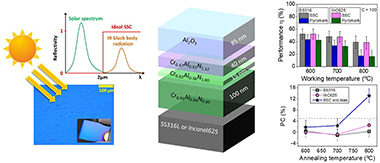
The effect of applying a negative bias during deposition of a previously designed multilayer solar selective absorber coating was studied on two types of substrates (316L stainless steel and Inconel 625). The solar selective coating is composed of different chromium aluminum nitride layers deposited using a combination of radiofrequency (RF), direct current (DC), and high-power impulse magnetron sputtering (HiPIMS) technologies. The chemical composition is varied to generate an infrared reflective/absorber layer (with low Al addition and N vacancies) and two CrAlN intermediate layers with medium and high aluminum content (Al/Cr = 0.6 and 1.2). A top aluminum oxide layer (Al2O3) is deposited as an antireflective layer. In this work, a simultaneous DC-pulsed bias (−100 V, 250 kHz) was applied to the substrates in order to increase the film density. The optical performance, thermal stability, and oxidation resistance was evaluated and compared with the performance obtained with similar unbiased coating and a commercial Pyromark paint reference at 600, 700, and 800 °C. The coating remained stable after 200 h of annealing at 600 °C, with solar absorptance (α) values of 93% and 92% for samples deposited on stainless steel and Inconel, respectively, and a thermal emittance ε25°C of 18%. The introduction of additional ion bombardment during film growth through bias assistance resulted in increased durability, thermal stability, and working temperature limits compared with unbiased coatings. The solar-to-mechanical energy conversion efficiency at 800 °C was found to be up to 2 times higher than Pyromark at C = 100 and comparable at C = 1000.
February, 2024 | DOI: 10.1021/acsaem.3c02310
Materiales Avanzados
Synthesis and characterization of porous and photocatalytic geopolymers based on natural clay: Enhanced properties and efficient Rhodamine B decomposition
Ettahiri, Y; Bouna, L: Brahim, A; Benlhachemi, A; Bakiz, B; Sánchez-Soto, PJ; Eliche-Quesada, D; Pérez-Villarejo, LApplied Materials Today, 36 (2024) 102048
Show abstract ▽
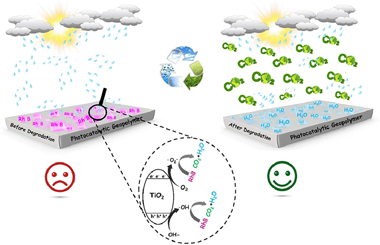
In this work, the incorporation of anatase TiO2 semiconductor in the geopolymer matrix as catalytic materials has been studied. The most noteworthy results obtained from the synthesis of a novel TiO2/geopolymer nanocomposite as an effective ecological catalyst with high thermal stability and significant porosity is presented. The porous and photocatalytic geopolymers based natural clay rich in pyrophyllite and kaolinite minerals were prepared by simple method, the geopolymerization reaction was able to successfully load TiO2 nanoparticles into the geopolymer surface. Furthermore, the results indicate that the prepared catalyst achieved the best performance to degrade Rhodamine B (RhB) molecules present in aqueous solution under UV light irradiation. The geopolymer matrix proved to be a reusable support for TiO2 nanoparticles during the photocatalytic process, efficiently facilitating the separation of photogenerated charges. Finally, the physicochemical and morphological properties of the samples was characterized by several techniques, namely X-ray Fluorescence (XRF), X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier Transform Infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), Thermogravimetric and Differential Thermal Analysis (TGA/DTA), N2 adsorption/desorption isotherm analysis (BET and BJH methods), UV–Vis Diffuse Reflectance Spectroscopy (DRS), Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) coupled to an Energy Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy (EDS) analyzer and Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM).
February, 2024 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apmt.2023.102048
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Renewable Carbonaceous Materials from Biomass in Catalytic Processes: A Review
Villora-Picó, JJ; González-Arias, J; Baena-Moreno, FM; Reina, TRMaterials, 17 (2024) 565
Show abstract ▽
This review paper delves into the diverse ways in which carbonaceous resources, sourced from renewable and sustainable origins, can be used in catalytic processes. Renewable carbonaceous materials that come from biomass-derived and waste feedstocks are key to developing more sustainable processes by replacing traditional carbon-based materials. By examining the potential of these renewable carbonaceous materials, this review aims to shed light on their significance in fostering environmentally conscious and sustainable practices within the realm of catalysis. The more important applications identified are biofuel production, tar removal, chemical production, photocatalytic systems, microbial fuel cell electrodes, and oxidation applications. Regarding biofuel production, biochar-supported catalysts have proved to be able to achieve biodiesel production with yields exceeding 70%. Furthermore, hydrochars and activated carbons derived from diverse biomass sources have demonstrated significant tar removal efficiency. For instance, rice husk char exhibited an increased BET surface area from 2.2 m2/g to 141 m2/g after pyrolysis at 600 °C, showcasing its effectiveness in adsorbing phenol and light aromatic hydrocarbons. Concerning chemical production and the oxidation of alcohols, the influence of biochar quantity and pre-calcination temperature on catalytic performance has been proven, achieving selectivity toward benzaldehyde exceeding 70%.
February, 2024 | DOI: 10.3390/ma17030565
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Growth dynamics of nanocolumnar thin films deposited by magnetron sputtering at oblique angles
Alvarez, R; Garcia-Valenzuela, A; Regodon, G; Ferrer, FJ; Rico, V; Garcia-Martin, JM; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Palmero, ANanotechnology, 35 (2024) 095705
Show abstract ▽
The morphology of numerous nanocolumnar thin films deposited by the magnetron sputtering technique at oblique geometries and at relatively low temperatures has been analyzed for materials as different as Au, Pt, Ti, Cr, TiO2, Al, HfN, Mo, V, WO3 and W. Despite similar deposition conditions, two characteristic nanostructures have been identified depending on the material: a first one defined by highly tilted and symmetric nanocolumnar structures with a relatively high film density, and a second one characterized by rather vertical and asymmetric nanocolumns, with a much lower film density. With the help of a model, the two characteristic nanostructures have been linked to different growth dynamics and, specifically, to different surface relaxation mechanisms upon the incorporation of gaseous species with kinetic energies above the surface binding energy. Moreover, in the case of Ti, a smooth structural transition between the two types of growths has been found when varying the value of the power used to maintain the plasma discharge. Based on these results, the existence of different surface relaxation mechanisms is proposed, which quantitatively explains numerous experimental results under the same conceptual framework.
February, 2024 | DOI: 10.1088/1361-6528/ad113d
- ‹ previous
- 3 of 410
- next ›














