Scientific Papers in SCI
2023
2023
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones - Reactividad de Sólidos
Effect of Alkaline Salts on Pyrolyzed Solid Wastes in Used Edible Oils: An Attenuated Total Reflectance Analysis of Surface Compounds as a Function of the Temperature
Romero-Sarria, F; Real, C; Córdoba, JM; Hidalgo, C; Alcalá, MDSpectroscopy Journal, 1 (2023) 98-110
Show abstract ▽
Biochars obtained via the pyrolysis of biomass are very attractive materials from the point of view of their applications and play key roles in the current energy context. The characterization of these carbonaceous materials is crucial to determine their field of application. In this work, the pyrolysis of a non-conventional biomass (solid wastes in used edible oils) was investigated. The obtained biochars were characterized using conventional techniques (TG, XRD, and SEM-EDX), and a deep analysis via ATR-FTIR was performed. This spectroscopic technique, which is a rapid and powerful tool that is well adapted to study carbon-based materials, was employed to determine the effect of temperature on the nature of functional groups on the surface. Moreover, the water washing of the raw sample (containing important quantities of inorganic salts) before pyrolysis evidenced that the inorganic salts act as catalysts in the biomass degradation and influence the degree of condensation (DOC) of PAH. Moreover, it was observed that these salts contribute to the retention of oxygenated compounds on the surface of the solid.
September, 2023 | DOI: 10.3390/spectroscj1020009
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Preparation, characterization and activation of Pd catalysts supported on CNx foam for the liquid phase decomposition of formic acid
Arzac, GM; Rojas, TC; Real, C; Fernández, AInternational Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 48 (2023) 31899-31613
Show abstract ▽
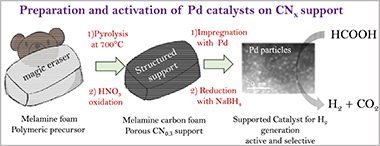
In this work, we have prepared a series of Pd catalysts on a CNx support for the liquid phase decomposition of formic acid. The structured CNx support was obtained through thermal pyrolysis of melamine foam and the pyrolysis conditions were optimized to achieve high surface area. The resulting support contains high amount of nitrogen with a contribution of pyridinic component. Several Pd catalysts were prepared and under optimized condi-tions, we were able to obtain small (2.7 +/- 0.9) nm Pd particles by using the oxidized support in powdery form. The activity of the optimized catalyst was studied under different con-ditions in the fresh and the used form. The fresh catalyst did not show significant activity. However, we found that the catalyst activated after use. Activation was understood in terms of the variation of surface Pd oxidation states under the effect of formic acid/sodium formate solutions. We found that the best activity is achieved under an optimal proportion of Pd0/PdII surface states according to previous reports. Under the best conditions, the activity of the best catalyst (8.6Pd/CN0.3) was as high as 9245 h-1, attributable to the small particle size, the Pd0/PdII ratio, the amount of pyridinic nitrogen, and the testing conditions, which included the preadsorption of sodium formate
September, 2023 | DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2023.04.244
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Cobalt Stabilization through Mesopore Confinement on TiO2 Support for Fischer-Tropsch Reaction
Platero, F; Todorova, S; Aoudjera, L; Michelin, L; Lebeau, B; Blin, JL; Holgado, JP; Caballero, A; Colón, GACS Applied Energy Materials, 6 (2023) 9475-9486
Show abstract ▽
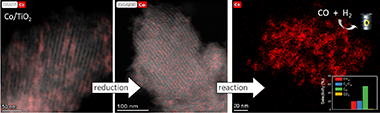
Cobalt supported on mesostructured TiO2 catalysts has been prepared by a wet-impregnation method. The Co/TiO2 catalytic system showed better catalytic performance after support calcination at 380 °C. Co nanoparticles appeared well distributed along the mesopore channels of TiO2. After reduction pretreatment and reaction, a drastic structural change leads to mesopore structure collapse and the dispersion of the Co nanoparticles on the external surface. Along this complex process, Co species first form discrete nanoparticles inside the pore and then diffuse out as the pore collapses. Through this confinement, a strong metal–support interaction effect is hindered, and highly stable metal active sites lead to better performance for Fischer–Tropsch synthesis reaction toward C5+ products.
September, 2023 | DOI: 10.1021/acsaem.3c01432
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Germination and First Stages of Growth in Drought, Salinity, and Cold Stress Conditions of Plasma-Treated Barley Seeds
Perea-Brenes, A; Garcia, JL; Cantos, M; Cotrino, J; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Gomez-Ramirez, A; López-Santos, CACS Agricultural Science & Technology, 3 (2023) 760-770
Show abstract ▽
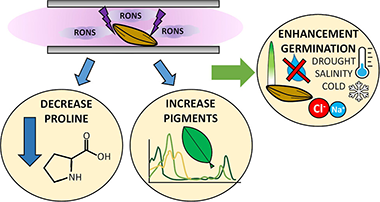
Numerous works have demonstrated that cold plasma treatments constitute an effective procedure to accelerate seed germination under nonstress conditions. Evidence also exists about a positive effect of plasmas for germination under environmental stress conditions. For barley seeds, this work studies the influence of cold plasma treatments on the germination rate and initial stages of plant growth in common stress environments, such as drought, salinity, and low-temperature conditions. As a general result, it has been found that the germination rate was higher for plasma-treated than for untreated seeds. Plasma also induced favorable changes in plant and radicle dimensions, which depended on the environment. The obtained results demonstrate that plasma affects the biochemical metabolic chains of seeds and plants, resulting in changes in the concentration of biochemical growing factors, a faster germination, and an initially more robust plant growth, even under stress conditions. These changes in phenotype are accompanied by differences in the concentration of biomarkers such as photosynthetic pigments (chlorophylls a and b and carotenoids), reactive oxygen species, and, particularly, the amino acid proline in the leaves of young plants, with changes that depend on environmental conditions and the application of a plasma treatment. This supports the idea that, rather than an increase in seed water imbibition capacity, there are clear beneficial effects on seedling of plasma treatments.
September, 2023 | DOI: 10.1021/acsagscitech.3c00121
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Plasma assisted dry reforming of methane: Syngas and hydrocarbons formation mechanisms
Navascues, P; Cotrino, J; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Gomez-Ramirez, AFuel Processing Technology, 248 (2023) 107827
Show abstract ▽
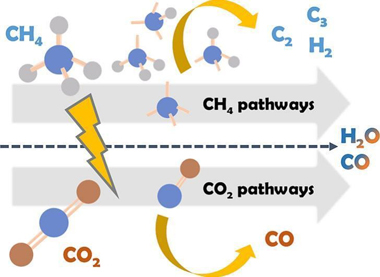
Plasma reactions of CO2 + CH4 mixtures have been proposed as a suitable process for the dry reforming of methane. Without specific catalysts, most studies report the formation of CO and H2 as main reaction products and arise the question whether CHx radicals coming from CH4 may interact with intermediate species formed by electron impact dissociation of CO2, a critical step for the formation of high added value oxygenated compounds. We have addressed this question studying the CO2 + CH4 plasma reaction in a ferroelectric-moderated packed -bed reactor varying the reactants ratio. Analysis of the reaction products by mass spectrometry and the plasma reaction intermediates by optical emission spectroscopy suggest that few direct cross-link interactions exist between intermediate plasma species issued from CH4 or CO2. This preliminary evidence is corroborated by experiments using 13CO2 instead 12CO2 as reactant. The isotope labeling procedure has proved that plasma re-action mechanisms of CO2 and CH4 molecules proceed almost independently, with the formation of small amounts of water and the removal of carbon deposits resulting CH4 plasma decomposition as sole evidences of cross reactions. These results highlight the need of using catalysts to promote specific surface reactions for a better control of the selectivity of the process.
September, 2023 | DOI: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2023.107827
- ‹ previous
- 13 of 410
- next ›














