Scientific Papers in SCI
2020
2020
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Recent advances in selective oxidation of biomass-derived platform chemicals over gold catalysts
Megias-Sayago, C; Navarro-Jaen, S; Castillo, R; Ivanova, SCurrent Opinion in Green and Sustainable Chemistry, 21 (2020) 50-55
Show abstract ▽
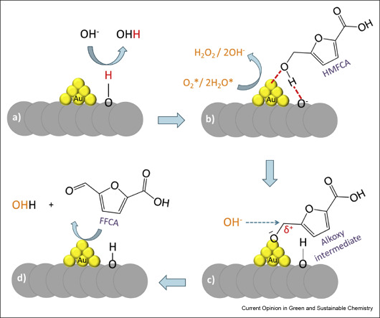
Gold is without a doubt the best known metal for chemical oxidation. The noblest of the noble metals gained its place because of its resistance to overoxidation, low temperature of operation, especially in gas-phase oxidation, and fairly good selectivity when required. The aim for sustainable development and the need for new technologies open the possibility to introduce new raw materials and new catalyst formulation. That is why new horizons appear in the otherwise uncertain future of gold catalysis. The old glory becomes now a glorious alternative, and this mini-review gives only a small example of it.
February, 2020 | DOI: 10.1016/j.cogsc.2019.12.001
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Role of Fe(III) in aqueous solution or deposited on ZnO surface in the photoassisted degradation of rhodamine B and caffeine
Tanji, Karim; Navio, J A; Martin-Gomez, A N; Hidalgo, M C; Jaramillo-Paez, C; Naja, Jamal; Hassoune, Hicham; Kherbeche, AbdelhakChemosphere, 241 (2020) 125009
Show abstract ▽
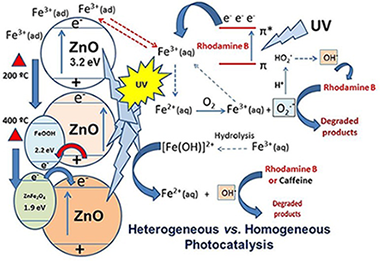
Iron (III) was incorporated, to the surface of a synthesized ZnO, using two nominal molar percentages of Fe (III): 1% and 5% Fe relative to ZnO. Samples dried and calcined at 200 °C and 400 °C for 2 h, were characterized by XRD, XPS, XRF, N2-adsorption-BET and (UV–vis)-DRS. Photocatalytic activities of the catalysts were assessed based on the degradation of rhodamine B (RhB) and caffeine (CAF) in aqueous solution under two irradiation conditions: UV and visible light illumination. Prior to the photocatalytic tests, the interaction of each one of the substrates with either Fe(III) or Fe(II) was studied in homogeneous medium under UV-illumination and oxygenated environment. It was found that Fe (III) can play an important role in homogeneous media in the photoassisted degradation, both of rhodamine B and caffeine, while Fe (II) does not exert a relevant role in the photoassisted degradation of the referred substrates. Fe–ZnO samples display similar or poorer performance than pure ZnO in the presence of UV light for both studied substrates. The phenomenon can be attributed to the formation of either goethite or ZnFe2O4 at the ZnO surface where the coupled Fe3+/Fe2+ can act as recombination centers for the photogenerated charges. On the contrary, all Fe–ZnO samples showed enhanced photocatalytic activity under visible illumination which seems to be independent of the iron content. In this context, the mechanisms for photoassisted degradation of both the substrates in homogeneous medium and photocatalytic degradation are discussed, as well as the role of Fe in the photodegradation processes.
February, 2020 | DOI: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125009
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Monolithic stirrer reactor: The selective lactose oxidation in liquid phase over Au/Al2O3 nanostructured catalysts
Regenhardt, SA; Meyer, CI; Sanz, O; Sebastian, V; Ivanova, S; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JA; Montes, M; Marchi, AJ; Garetto, TFMolecular Catalysis, 481 (2020) 110219
Show abstract ▽
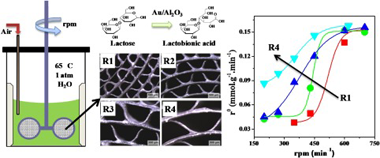
The performance of rotating metallic monolith stirrer reactor was studied for selective lactose oxidation in liquid phase at 65 degrees C, atmospheric pressure and with air as oxidant agent. The Au/Al(2)O(3)deposition on metallic substrates was performed by wash-coating, producing catalyst coating thicknesses between 5 and 20 mu m. Monoliths with different configuration (channel size between 0.36 and 1.06 mm) were used as stirrer blades in a batch reactor. Internal and external mass transfer limitations were observed during liquid phase lactose oxidation. For stirring rates equal or higher than 600 rpm there were no important external diffusional restrictions and this was also independent of the monolith configuration. Coating with thickness higher than 15 mu m presents loss of catalyst effectiveness due to internal diffusional restrictions. Excellent stability in the catalytic tests was obtained after three regeneration-reaction cycles. Regeneration was carried out at 400 degrees C in air flow. Gold particle size distribution in the monolith washcoat, determined by TEM before and after reaction, was homogeneous with a medium size of around 5 nm. This is in agreement with the very good reproducibility and stability obtained in the catalytic tests. After calcination at 500 degrees C, some sintering and a heterogeneous distribution of metal particle size was observed, accompanied by a slight loss in catalyst activity. It is concluded that metallic monolith stirrer reactors are a promising application for selective lactose oxidation in liquid phase.
February, 2020 | DOI: 10.1016/j.mcat.2018.10.014
Reactividad de Sólidos
Development of Ti(C,N)-based cermets with (Co,Fe,Ni)-based high entropy alloys as binder phase
de la Obra, AG; Sayagues, MJ; Chicardi, E; Gotor, FJJournal of Alloys and Compounds, 814 (2020) 152218
Show abstract ▽
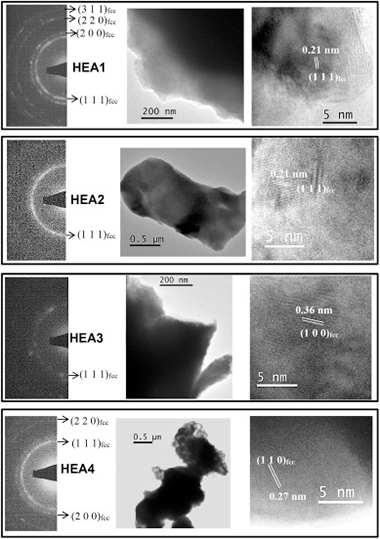
High entropy alloys have been proposed as novel binder phases in cemented carbides and cermets. Many aspects related to the stability of these alloys during the liquid phase sintering process are still unclear and were addressed in this work. Consolidated Ti(C,N)-based cermets using four different (Co,Fe,Ni)based high entropy alloys as the binder phase were obtained. The chosen alloys - CoCrCuFeNi, CoCrFeNiV, CoCrFeMnNi and CoFeMnNiV - were previously synthesized through mechanical alloying and a single alloyed solid solution phase with fcc structure and nanometric character was always obtained. The powdered alloys and the consolidated cermets were analyzed by X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, X-ray energy dispersive spectrometry and transmission electron microscopy. Differential thermal analysis was employed to determine the melting point of the four high entropy alloys that ranged between 1310 degrees C and 1375 degrees C. Although a high temperature of 1575 degrees C was required to obtain the highest cermet densification by pressureless sintering, porosity still remained in most of the cermets. Best densification was achieved when CoCrFeNiV was used as the binder phase. During liquid phase sintering, different compositional changes were observed in the ceramic and binder phases. A core-rim microstructure was observed in cermets containing V in the alloys (CoCrFeNiV and CoFeMnNiV), since this element was incorporated to the carbonitride structure during sintering. A slight Cr segregation was detected in cermets containing Cr, leading to CrTi-rich alloys in small binder regions. However, a great Cu segregation was produced when CoCrCuFeNi was used, and the formation of two different fcc alloys -a Cu-rich and a Cu-depleted- was observed. Finally, a loss of Mn was also evidenced in CoCrFeMnNi and CoFeMnNiV, probably due to its sublimation at the sintering temperature.
January, 2020 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.152218
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Preparation and Characterization of Bio-Based PLA/PBAT and Cinnamon Essential Oil Polymer Fibers and Life-Cycle Assessment from Hydrolytic Degradation
Correa-Pacheco, ZN; Black-Solis, JD; Ortega-Gudino, P; Sabino-Gutierrez, MA; Benitez-Jimenez, JJ; Barajas-Cervantes, A; Bautista-Banos, S; Hurtado-Colmenares, LBPolymers, 12 (2020) 38
Show abstract ▽

Nowadays, the need to reduce the dependence on fuel products and to achieve a sustainable development is of special importance due to environmental concerns. Therefore, new alternatives must be sought. In this work, extruded fibers from poly (lactic acid) (PLA) and poly (butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) (PBAT) added with cinnamon essential oil (CEO) were prepared and characterized, and the hydrolytic degradation was assessed. A two-phase system was observed with spherical particles of PBAT embedded in the PLA matrix. The thermal analysis showed partial miscibility between PLA and PBAT. Mechanically, Young's modulus decreased and the elongation at break increased with the incorporation of PBAT and CEO into the blends. The variation in weight loss for the fibers was below 5% during the period of hydrolytic degradation studied with the most important changes at 37 degrees C and pH 8.50. From microscopy, the formation of cracks in the fiber surface was evidenced, especially for PLA fibers in alkaline medium at 37 degrees C. This study shows the importance of the variables that influence the performance of polyester-cinnamon essential oil-based fibers in agro-industrial applications for horticultural product preservation.
January, 2020 | DOI: 10.3390/polym12010038
- ‹ previous
- 107 of 410
- next ›














